- Introduction
- Getting Started
- Gitpod Tutorial
- Use Cases
- Languages
- Configure
- Workspaces
- User settings
- Repositories
- Organizations
- Authentication
- Billing
- References
- .gitpod.yml
- IDEs & editors
- Integrations
- Gitpod CLI
- Gitpod API
- Gitpod URL
- Compatibility
- Enterprise
- Guides
- Background
- Reference
- Help
- Contribute
- Troubleshooting
.gitpod.yml
The .gitpod.yml file instructs Gitpod on how to prepare and build a project, such as starting development servers and configuring Prebuilds. Below is a full reference of all available properties. To see the underlying schema, please refer to gitpod-io/gitpod in the gitpod-io/gitpod repository.
For a more comprehensive configuration guide, see configuring a project.
- .gitpod.yml
additionalRepositories
additionalRepositories is currently in Beta. Send feedback.
Defines additional source control repositories to clone and where the repository is cloned under /workspaces
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object |
<empty> |
Demo
Example
additionalRepositories:
- url: https://github.com/gitpod-io/demo-multi-repo-backend
# checkoutLocation is optional and relative to /workspaces.
# by default the location defaults to the repository name.
checkoutLocation: backendWhen the above configuration is defined then the following additional steps happen when Gitpod workspace is started:
- If you open a workspace on a branch, Gitpod will clone the same-named branch in all repositories. If such a branch doesn’t exist Gitpod checks out the default branch.
- The contents of the branch is cloned under
/workspaces/ - The contents of
https://github.com/gitpod-io/demo-multi-repo-backendis cloned to/workspaces/backend
After all of the source control repositories have been cloned then the before, init and command tasks are executed as per normal.
If you need to run commands (such as package installation or compilation) on the source control repositories which have been cloned then change your working directory to the use configured or default checkoutLocation location using the before task.
Example
# example .gitpod.yml from https://github.com/gitpod-io/demo-multi-repo-frontend
additionalRepositories:
- url: https://github.com/gitpod-io/demo-multi-repo-backend
# checkoutLocation is optional and relative to /workspaces.
# by default the location defaults to the repository name.
checkoutLocation: backend
tasks:
- name: backend
# change working directory as per configured in `checkoutLocation`
# which is configured above as `/workspaces/backend`
before: |
cd ../backend
init: |
echo npm install
command: |
echo npm run dev
# changing of working directory is not required as these tasks will
# by default by executed in `/workspaces/demo-multi-repo-frontend`
- name: frontend
init: |
echo npm install
echo npm run build
command: |
echo npm run devcheckoutLocation
Define where Gitpod checks out the project’s code, relative to /workspace.
In most cases, this is not needed. If you work on an older Go project, please see the Go Language Page for more details.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
/workspace |
Example
checkoutLocation: 'go/src/github.com/demo-apps/go-gin-app'coreDump
Define workspace core dump behavior.
For most cases, setting the coreDump property is not required. However, it can be a valuable feature to debug C++, or when debugging add-ons in Rust, Python, or node.js.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object |
<empty> |
Example
coreDump:
enabled: trueYou can also set custom size values for the generated core files using the softLimit and hardLimit values (see example below). The setting softLimit configures the upper limit on the size of the core dump file that will be produced if a process receives a core dump signal, while hardLimit allows setting a hard limit to act as a ceiling for the soft limit.
coreDump:
enabled: true
softLimit: <bytes>
hardLimit: <bytes>For more details, please see the Linux man page for getrlimit
gitConfig
Define a workspace’s git configuration as key-value pairs.
Please refer to https://git-scm.com/docs/git-config#_values for a list of accepted values.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object |
<empty> |
Example
gitConfig:
alias.st: status
core.autocrlf: inputgithub
Configure the GitHub Gitpod app. At this time, the following configuration is used to configure continuous prebuilds for GitHub repositories.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object |
<empty> |
Example
github:
prebuilds:
master: true
branches: true
pullRequests: true
pullRequestsFromForks: true
addCheck: false
addComment: false
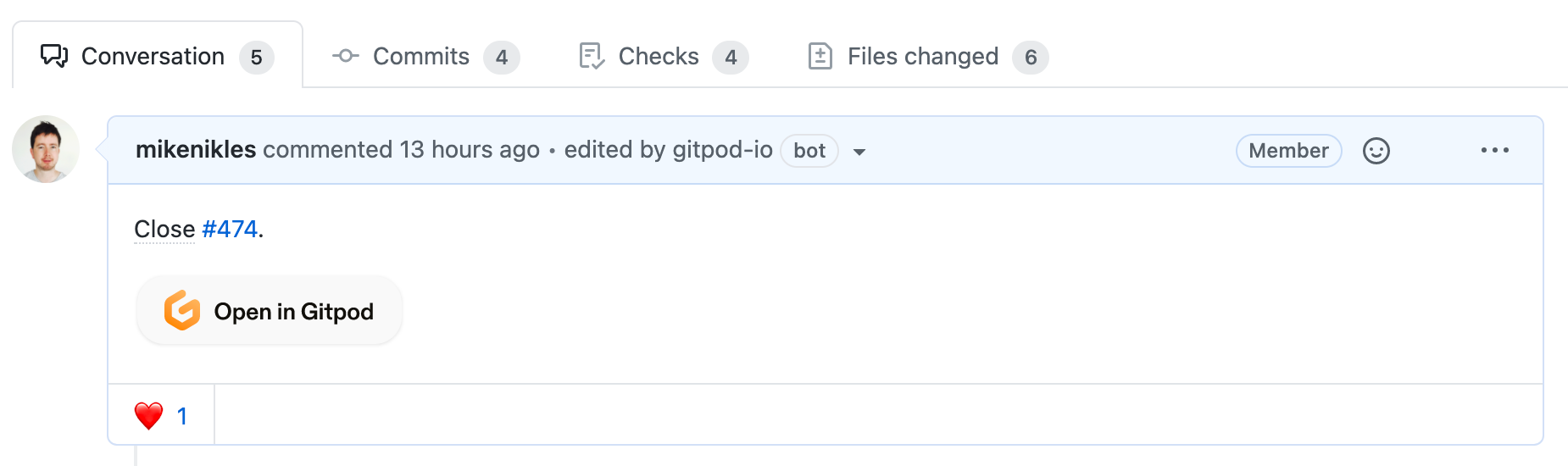
addBadge: trueprebuilds.addBadge
Gitpod can modify the description of a pull request to add an “Open in Gitpod” button. This approach produces fewer GitHub notifications than adding a comment, but can also create a concurrent editing conflict when the bot and a user try to edit the description of a pull request at the same time.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
boolean |
false |
prebuilds.addCheck
Configure whether Gitpod registers itself as a status check to pull requests - much like a continuous integration system would do. By default a failing prebuild would not make the check fail. Set prevent-merge-on-error to block PR merging when prebuilds failed.
To learn more about status checks, please see the GitHub documentation about status checks.
| Type | Default | Values |
|---|---|---|
string |
prevent-merge-on-error |
true, false, prevent-merge-on-error |
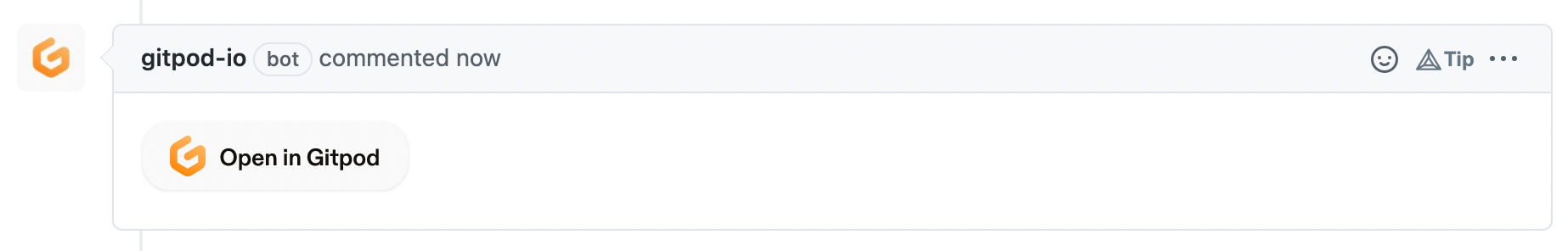
prebuilds.addComment
Gitpod can add a comment with an “Open in Gitpod” button to your pull requests. Alternatively, you could add a badge to the pull request’s description.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
boolean |
false |
prebuilds.addLabel
Deprecated.
prebuilds.branches
Define whether Gitpod creates prebuilds for all branches.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
boolean |
false |
prebuilds.master
Define whether Gitpod creates prebuilds for the default branch.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
boolean |
true |
prebuilds.pullRequests
Define whether Gitpod creates prebuilds for pull requests from the original repository.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
boolean |
true |
prebuilds.pullRequestsFromForks
Define whether Gitpod creates prebuilds for pull requests from forks.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
boolean |
false |
image
Define a custom Docker image to be used for workspaces. To learn more, please review Custom Docker Image.
Public images are hosted on Docker Hub and can be referenced by their name, e.g. ubuntu:latest.
To see a list of Gitpod-provided images, please see gitpod-io/workspace-images.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object or string |
gitpod/workspace-full |
Examples
With a public image
image: ubuntu:latestWith a custom image
image:
file: .gitpod.DockerfileWith an optional context
image:
file: .gitpod.Dockerfile
context: ./docker-contentimage.file
To define a custom Docker image, you can use the following configuration:
For a list of examples, please see https://github.com/gitpod-io/workspace-images.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
image.context
Optionally, you can set the image.context. This is useful when you want to copy files into the Docker image. The Docker docs describe this in more detail.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
jetbrains
JetBrains is currently in Beta · Send feedback.
Define the integration between Gitpod and JetBrains IDEs.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object |
<empty> |
jetbrains.plugins
JetBrains plugin support (via gitpod.yml) is currently in Beta · Send feedback.
Define a list of plugins which should be installed for all compatible JetBrains IDEs when starting a workspace. To find the plugin identifier, from the JetBrains Marketplace, find the desired plugin, open the ‘Versions’ tab, select any version and copy the ‘Plugin ID’ (like ${publisher}.${name}).
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
array |
<empty> |
jetbrains.[product]
JetBrains is currently in Beta · Send feedback.
Define the integration between Gitpod and a specific JetBrains IDE. Install plugins and configure prebuilds to speed up the IDE indexing.
Specify the ‘product’ with one of the following values:
intellijgolandpycharmphpstorm
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object |
<empty> |
jetbrains.[product].plugins
JetBrains plugin support (via gitpod.yml) is currently in Beta · Send feedback.
Define a list of plugins which should be installed for the given JetBrains IDE when starting a workspace. To find the plugin identifier, from the JetBrains Marketplace, find the desired plugin, open the ‘Versions’ tab, select any version and copy the ‘Plugin ID’ (like ${publisher}.${name}).
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
array |
<empty> |
Example
jetbrains:
intellij:
plugins:
- zielu.gittoolbox
- izhangzhihao.rainbow.bracketsjetbrains.[product].prebuilds
JetBrains prebuilds support (via gitpod.yml) is currently in Alpha · Send feedback.
Define whether Gitpod enables prebuilds for a specific JetBrains IDE.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object |
<empty> |
Example
jetbrains:
intellij:
prebuilds:
version: stableThe version is defined as follows:
| Type | Default | Values |
|---|---|---|
string |
stable |
stable, latest, both |
jetbrains.[product].vmoptions
Configuration of JVM options (via gitpod.yml) is currently in Alpha · Send feedback.
Configure JVM options for a specific JetBrains IDE.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
Example
jetbrains:
intellij:
vmoptions: '-Xmx4g'ports
Configure how Gitpod treats various ports your application may listen on. You can learn more about this in the Exposing Ports documentation.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
array |
<empty> |
Example
ports:
- name: Website
port: 3000
onOpen: open-preview
- name: VNC
description: full GUI Virtual Desktop
port: 6080
onOpen: open-browser
- name: Server
port: 10000
onOpen: ignoreports[n].name
Define a name for the port, which will be shown as a column in the output of gp ports list and in the Port column inside of the ports list in VS Code Browser and Desktop.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
ports[n].description
Adds a description to the port, which will be shown as a column in the output of gp ports list.
You can find the port’s description in the ports view table column, following the Address field (the same description can be found in the Remote Explorer as a tooltip [on hover] of the port).
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
ports[n].onOpen
Define what to do when Gitpod detects a given port is being listened on.
| Type | Default | Values |
|---|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
open-browser,open-preview,notify,ignore |
Please note: For JetBrains IDEs connected to Gitpod via JetBrains Gateway open-preview will behave exactly the same as open-browser, as there is no functionality for a web preview in the JetBrains IDE.
ports[n].port
Define a single port or a range of ports, e.g. 3000-3100.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
number or string |
<empty> |
ports[n].visibility
Define whether to expose the port publicly or keep it private.
A public port allows you to share a URL for a given port with team members, for example if you want to get their feedback on a new feature you develop.
| Type | Default | Values |
|---|---|---|
string |
private |
private,public |
ports[n].protocol
Define whether a running port in the workspace is HTTP or HTTPS.
| Type | Default | Values |
|---|---|---|
string |
http |
http, https |
tasks
Define how Gitpod prepares & builds your project and how it can start the project’s development server(s). To learn more, please visit Start Tasks. Each array element opens in its own terminal.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
array |
<empty> |
Example
tasks:
- before: sh ./scripts/setup.sh
init: npm install
command: npm run dev
- name: Database
init: sh ./scripts/seed-database.sh
command: npm start-db
env:
DB_HOST: localhost:3306
DB_USER: readOnlyUsertasks[n].before
A shell command to run before init and the main command. This command is executed on every start and is expected to terminate. If it fails, the following commands will not be executed.
Learn more about Start Tasks in the docs.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
tasks[n].command
The main shell command to run after before and init. This command is executed last on every start and doesn’t have to terminate.
Learn more about Start Tasks in the docs.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
tasks[n].env
Define environment variables that will be available in the workspace.
Learn more about Environment Variables in the docs.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object |
<empty> |
tasks[n].init
A shell command to run between before and the main command.
This task is executed only once. When you start a workspace that does not have a prebuild, init is executed at workspace start. When you start a workspace that has a prebuild, init executes as part of the prebuild, but does NOT execute again at workspace start.
This task is expected to terminate. If it fails, the command property will not be executed.
Learn more about Start Tasks in the docs.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
tasks[n].name
A name for the task, also shown on the terminal tab.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
tasks[n].openIn
Deprecated. This does not have an impact in VS Code.
tasks[n].openMode
Configure how the terminal should be opened relative to the previous task.
| Type | Default | Values |
|---|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
tab-after,tab-before,split-right,split-left |
Note: split-top and split-bottom are deprecated values.
tasks[n].prebuild
Deprecated. Please use the init task instead.
mainConfiguration
mainConfiguration is currently in Beta. Send feedback.
Defines the repository with the main .gitpod.yml file and makes it possible to open the same workspace from any issue, branch or other context URL from any repository defined in a multi repository configuration.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
<empty> |
Demo
Example
mainConfiguration: https://github.com/gitpod-io/demo-multi-repo-frontendvscode
Configure the VS Code editor.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object |
<empty> |
vscode.extensions
Define a list of extensions which should be installed for users of this workspace. The identifier of an extension is always ${publisher}.${name}. For example: ‘vscodevim.vim’.
Please note, Gitpod uses the Open VSX registry to find extensions. If you cannot find an extension you know exists in your local VS Code, please get in touch with us or open a new PR in the open-vsx/publish-extensions repository to add the extension to Open VSX 🙏.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
object |
<empty> |
By default, extensions will use the latest available version unless you use a specific version number. The version number must use semantic versioning rules. If you are interested in importing an extension that is not published on the Open VSX registry you can directly use the full URL.
Example
vscode:
extensions:
- svelte.svelte-vscode
- bradlc.vscode-tailwindcss@0.6.11
- https://example.com/abc/releases/extension-0.26.0.vsixworkspaceLocation
Define which path Gitpod considers the project’s workspace directory, relative to /workspace.
In most cases, this is not needed. If you work on an older Go project, please see the Go Languages page for more details.
| Type | Default |
|---|---|
string |
/workspace |
Example
workspaceLocation: '.'