Enterprise CloudFormation templates v1
Getting Started with Enterprise CloudFormation templates v1
Request your Enterprise trial
us-east-1us-east-2us-west-2ap-northeast-1ap-southeast-2eu-west-1eu-west-2eu-west-3eu-central-1sa-east-1
0. Prerequisites
Here’s a list of what you’ll need to get started with Enterprise:- An AWS account. For a production installation, there should be no other resources, EC2 instances, containers, functions or applications running in the account. For a pre-production (e.g. proof-of-concept) installation, other resources may be running in the account, however this does introduce a risk of interference with the running installation - please speak to your Gitpod account manager. If your company requires security policies or roles to be present in new accounts please review them with a Gitpod Engineer to ensure there are no items that will block Enterprise from running.
- Private network address ranges. Provide a list of network CIDR ranges to your Gitpod engineer to ensure that traffic is routed correctly to internal resources. This list should include the network address space for any internal or on-premise networks that developers will need to access from their Gitpod workspaces.
- List of resources developers require to build and test. This should include any external databases, APIs, PaaS endpoints, cloud resources and anything else that your developers need to build and test their code. Review this list with your Gitpod engineer to ensure the right architecture is set up for your installation. Enterprise has four supported modes - public, private, mixed public, and mixed private. We will help you choose the right mode for your environment.
- The ability to run an AWS Cloudformation template. The Enterprise installer is provided as a set of Cloudformation templates. These should be run by a user with Administrator level access to the AWS account. We do not support running the Cloudformation template through terraform. You may run the Cloudformation templates either in the AWS Console (recommended) or via the AWS CLI (expert).
- Optional - AWS Transit Gateway. For private, mixed private, and mixed public installations you will create a transit gateway attachment that allows workspaces to connect to private resources on your network. Work with your Gitpod engineer to get this set up correctly.
1. Set up an AWS Account for Enterprise
| Service | Name | Value | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|---|
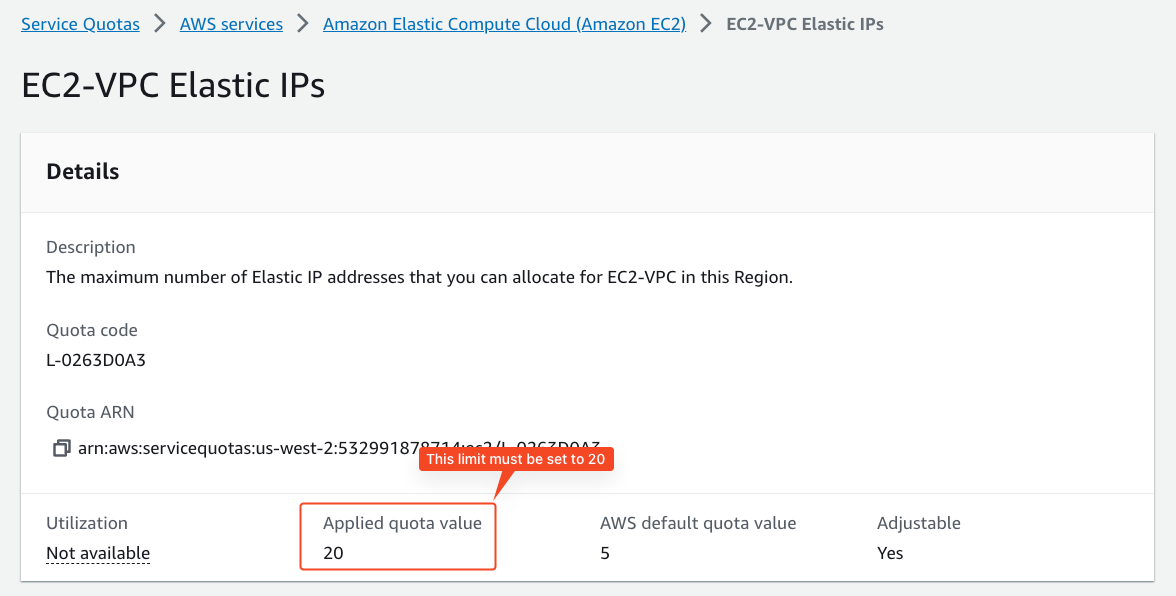
| Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) | EC2-VPC Elastic IPs | 20 | Gitpod requires 3 IP addresses for each load balancer (Gitpod has 2 load balancers, one for meta and one for the workspace cluster). Additionally, 3 IPs are needed for each NAT gateway (Gitpod has 3 VPCs, so 3x). Therefore, at a minimum, 15 IPs are needed. The additional 5 act as a buffer in case a new load balancer needs to be provisioned and runs in parallel to the old one, ensuring a smooth transition. For more information, please see Architecture. |
| Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) | Running On-Demand Standard (A, C, D, H, I, M, R, T, Z) Instances | 256 | This value depends on the number of concurrent developers using the instance. 256 the minimum recommended setting and is suitable for proof-of-value trials. Consult with your engineer on an appropriate setting for your expected usage levels. |
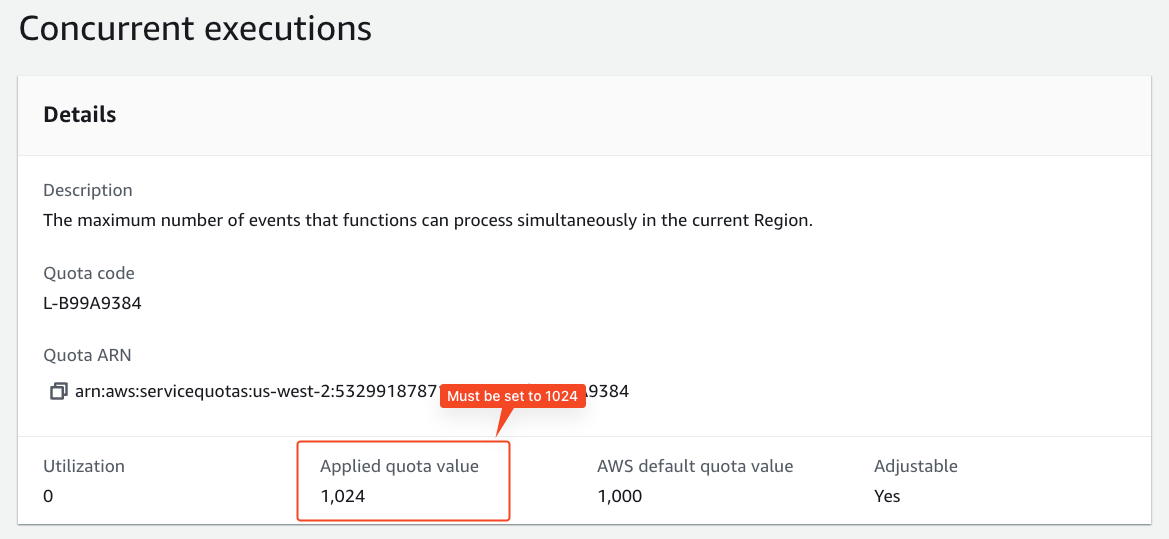
| AWS Lambda | Concurrent Executions | 1024 | To ensure Gitpod can install and operate properly, the default concurrent execution quota should be increased to 1024. Increasing the quota to 1024 guarantees that Gitpod will function properly. |
| Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) | VPCs per Region | 4 | Enterprise requires four VPCs. One is the default VPC that comes pre-installed in new accounts. The Enterprise platform runs in a second VPC. The other two VPCs are reserved for upcoming feature enhancements. |
Click to view screenshot: Elastic IPs
Click to view screenshot: Elastic IPs
Click to view screenshot: Lambdas
Click to view screenshot: Lambdas
eu-central-1. For example, this could be restricted by SCPs such as a Region deny SCP. To roll out updates to the application, an AWS Lambda function pulls several configurations from a known S3 bucket owned by Gitpod. This bucket is hosted in the Enterprise control plane located in the eu-central-1 region.
2. Execute two CloudFormation templates
2.1 Provide information
Your Gitpod account manager will ask for information needed to generate the CloudFormation templates used to install Gitpod. The information required depends on the choice of networking mode. To help choose the right networking mode, please see Networking and Data flows for general guidance and requirements on which services Gitpod needs to be able to route to. This flow chart helps select the right networking mode: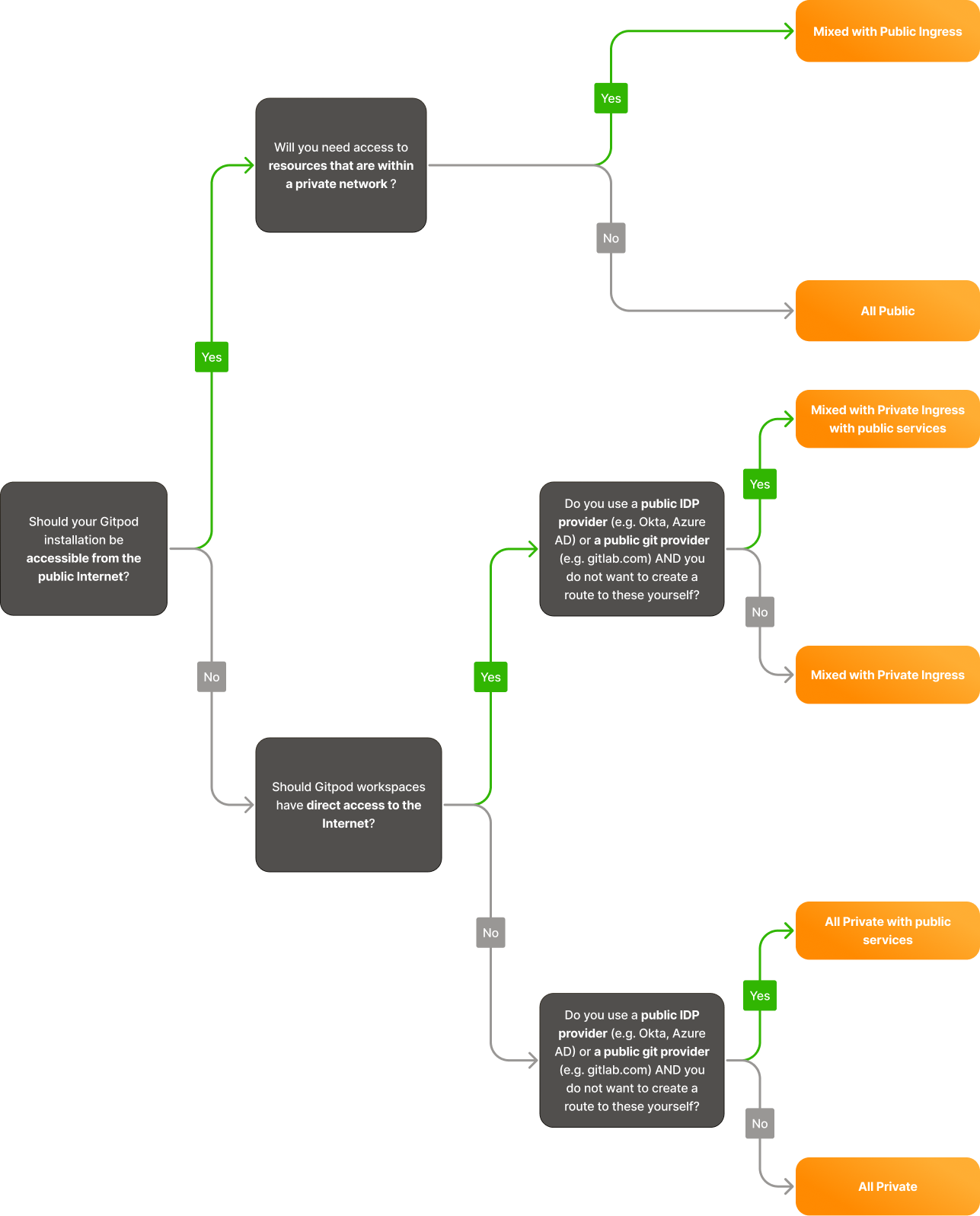
Networking Modes Flowchart
All Private Networking Mode
All Private Networking Mode
-
Subdomainof your Gitpod installation. The full domain will be<subdomain>.gitpod.cloudunless a custom domain is used (see below).Note on compliance and privacy
Depending on your compliance and regulatory requirements, you may want to avoid including your company name in the URL. Although efforts are taken to minimize any exposure, avoiding using the company name can further increase confidentiality and reduce exposure risk. -
AWS account IDof the AWS account to be used for Gitpod. -
AWS regionwhere Gitpod will be installed. See above for available regions. -
Relay CIDR range: The small part of the Enterprise VPC that needs to be routable from your network. This is called the relay subnet and it attaches to your Transit Gateway (see below). See Networking and Data flows for more details and a networking diagram.Please consider the following points when choosing this range
- The only restriction in place is that the
Relay CIDR rangemust be/25and not in the range100.70.0.0/10(the parent range used by Gitpod). - The
Relay CIDR rangeFor example, your source code repository, SSO provider, or package repositories. - The
Relay CIDR rangemust be routable from your source code repository (SCM) server for Prebuilds to work. Prebuilds are powered by webhooks, so Gitpod must be able to get notifications of changes to your code repos to trigger prebuilds.
- The only restriction in place is that the
-
CIDR range of your networkor the IP address space used by your company network that you want workspaces to be able to route to. At the very least, provide the relevant ranges that you want Gitpod to be able to interact with. This helps Gitpod ensure there are no possible IP conflicts with CIDR ranges used internally in the Gitpod instance (100.70.0.0/16, part of CGNAT range). Note that this internal Gitpod range does not need to be routable from your network. -
transitGatewayIDof your Transit Gateway. Network traffic to your internal resources will be routed through a new transit gateway attachment. Enterprise control plane traffic does not route through the transit gateway, it is reserved for your internal traffic. See Networking and Data flows for more information.
Note on auto propagation
Note on auto propagation
Expose public services?: This optional feature may be enabled to expose webhooks and Identity Provider (IDP) services on public endpoints. The added API gateway does not expose your entire instance to the public Internet. This can be helpful for connecting to OIDC providers such as Okta, Azure AD. This option also makes it easy for developers to connect to your instance without having to route through a VPN or transit gateway.
Mixed with Private Ingress Networking Mode
Mixed with Private Ingress Networking Mode
Subdomainof your Gitpod installation. The full domain will be<subdomain>.gitpod.cloudunless a custom domain is used (see below).
Note on compliance and privacy
Note on compliance and privacy
AWS account IDof the AWS account to be used for Gitpod.AWS regionwhere Gitpod will be installed. See above for available regions.Relay CIDR range: The small part of the Enterprise VPC that needs to be routable from your network. This is called the relay subnet and it attaches to your Transit Gateway (see below). See Networking and Data flows for more details and a networking diagram.
Please consider the following points when choosing this range
Please consider the following points when choosing this range
- The only restriction in place is that the
Relay CIDR rangemust be/25and not in the range100.70.0.0/10(the parent range used by Gitpod). - The
Relay CIDR rangeFor example, your source code repository, SSO provider, or package repositories. - The
Relay CIDR rangemust be routable from your source code repository (SCM) server for Prebuilds to work. Prebuilds are powered by webhooks, so Gitpod must be able to get notifications of changes to your code repos to trigger prebuilds.
-
CIDR range of your networkor the IP address space used by your company network that you want workspaces to be able to route to. It is essential to provide the relevant ranges that you want Gitpod to be able to interact with. At a minimum, this should include the CIDR range of the VPC where the transit gateway associated with Gitpod is deployed, as this ensures Gitpod can identify the route back to the origin of its connections. Providing these CIDR ranges also helps Gitpod ensure there are no possible IP conflicts with CIDR ranges used internally in the Gitpod instance (100.70.0.0/16, part of CGNAT range). Note that this internal Gitpod range does not need to be routable from your network. -
transitGatewayIDof your Transit Gateway. Network traffic to your internal resources will be routed through a new transit gateway attachment. Enterprise control plane traffic does not route through the transit gateway, it is reserved for your internal traffic. See Networking and Data flows for more information.
Note on auto propagation
Note on auto propagation
Expose public services?: This optional feature may be enabled to expose webhooks and Identity Provider (IDP) services on public endpoints. The added API gateway does not expose your entire instance to the public Internet. This can be helpful for connecting to OIDC providers such as Okta, Azure AD. This option also makes it easy for developers to connect to your instance without having to route through a VPN or transit gateway.
Mixed with Public Ingress Networking Mode
Mixed with Public Ingress Networking Mode
Subdomainof your Gitpod installation. The full domain will be<subdomain>.gitpod.cloudunless a custom domain is used (see below).
Note on compliance and privacy
Note on compliance and privacy
AWS account IDof the AWS account to be used for Gitpod.AWS regionwhere Gitpod will be installed. See above for available regions.Relay CIDR range: The small part of the Enterprise VPC that needs to be routable from your network. This is called the relay subnet and it attaches to your Transit Gateway (see below). See Networking and Data flows for more details and a networking diagram.
Please consider the following points when choosing this range
Please consider the following points when choosing this range
- The only restriction in place is that the
Relay CIDR rangemust be/25and not in the range100.70.0.0/10(the parent range used by Gitpod). - The
Relay CIDR rangeFor example, your source code repository, SSO provider, or package repositories. - The
Relay CIDR rangemust be routable from your source code repository (SCM) server for Prebuilds to work. Prebuilds are powered by webhooks, so Gitpod must be able to get notifications of changes to your code repos to trigger prebuilds.
-
CIDR range of your networkor the IP address space used by your company network that you want workspaces to be able to route to. At the very least, provide the relevant ranges that you want Gitpod to be able to interact with. This helps Gitpod ensure there are no possible IP conflicts with CIDR ranges used internally in the Gitpod instance (100.70.0.0/16, part of CGNAT range). Note that this internal Gitpod range does not need to be routable from your network. -
transitGatewayIDof your Transit Gateway. Network traffic to your internal resources will be routed through a new transit gateway attachment. Enterprise control plane traffic does not route through the transit gateway, it is reserved for your internal traffic. See Networking and Data flows for more information.
Note on auto propagation
Note on auto propagation
All Public Networking Mode
All Public Networking Mode
Subdomainof your Gitpod installation. The full domain will be<subdomain>.gitpod.cloudunless a custom domain is used (see below).
Note on compliance and privacy
Note on compliance and privacy
AWS account IDof the AWS account to be used for Gitpod.AWS regionwhere Gitpod will be installed. See above for available regions.
When using an Allowlist
When using an Allowlist
-
allowlistof IPs or CIDR ranges that should be allowed to access the instance. Any CIDRs provided in theCIDR range of your networkabove are always allowed. Example:
When using a Custom Domain
When using a Custom Domain
domainNamethat is to be usedARN of the certificateto be used
When using certificates signed by a custom or private Certificate Authority
When using certificates signed by a custom or private Certificate Authority
2.2 Receive your Cloudformation Templates
You will need to execute two CloudFormation templates to install the infrastructure and subsequently Enterprise:-
gitpod-roleTemplate: This template creates a new IAM role with specific policies attached. These policies grant the minimum permissions necessary to install and run Enterprise in your account. -
gitpod-instanceTemplate: This template installs the infrastructure for Enterprise. The role created by thegitpod-roletemplate is used to execute this second template.
2.3 Execute CloudFormation templates
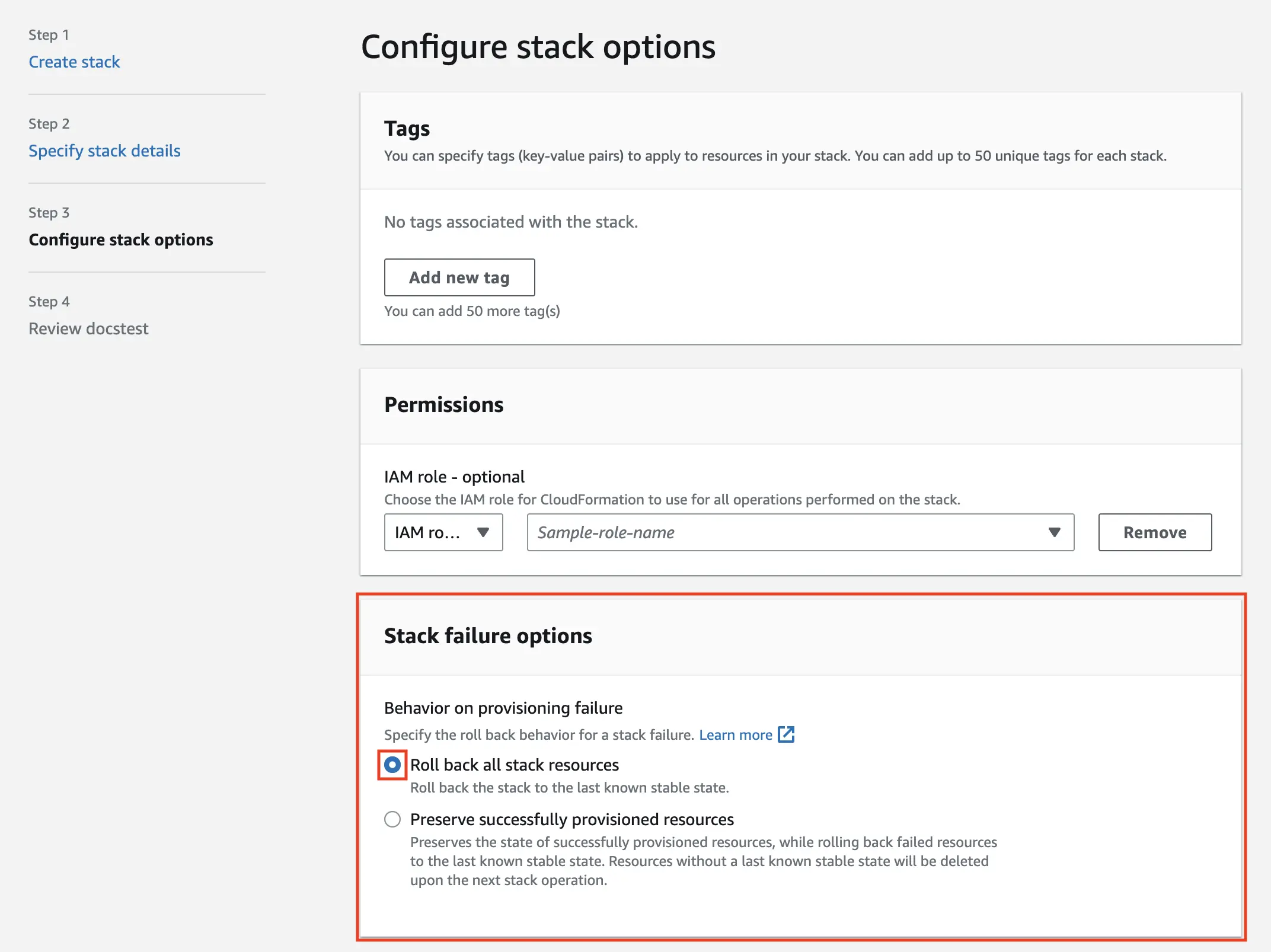
- First, execute the
gitpod-roletemplate by navigating to the link shared by your Gitpod Account Manager. During the “configure stack options” step, ensure you select the “roll back all the stack resources” option under “Stack failure options”. This will ensure that all resources created by the template are deleted if the template fails to execute.
- Then, execute
gitpod-instancetemplate also by navigating to the link shared by your Gitpod Account Manager in the same AWS account. This will create the infrastructure that Enterprise requires.
GitpodSetupAndInitialEKSUserAdmin) as the role used
for permissions. Depending on timing, you may need to manually select the role
using its ARN. Again, select the “roll back all the stack resources” option.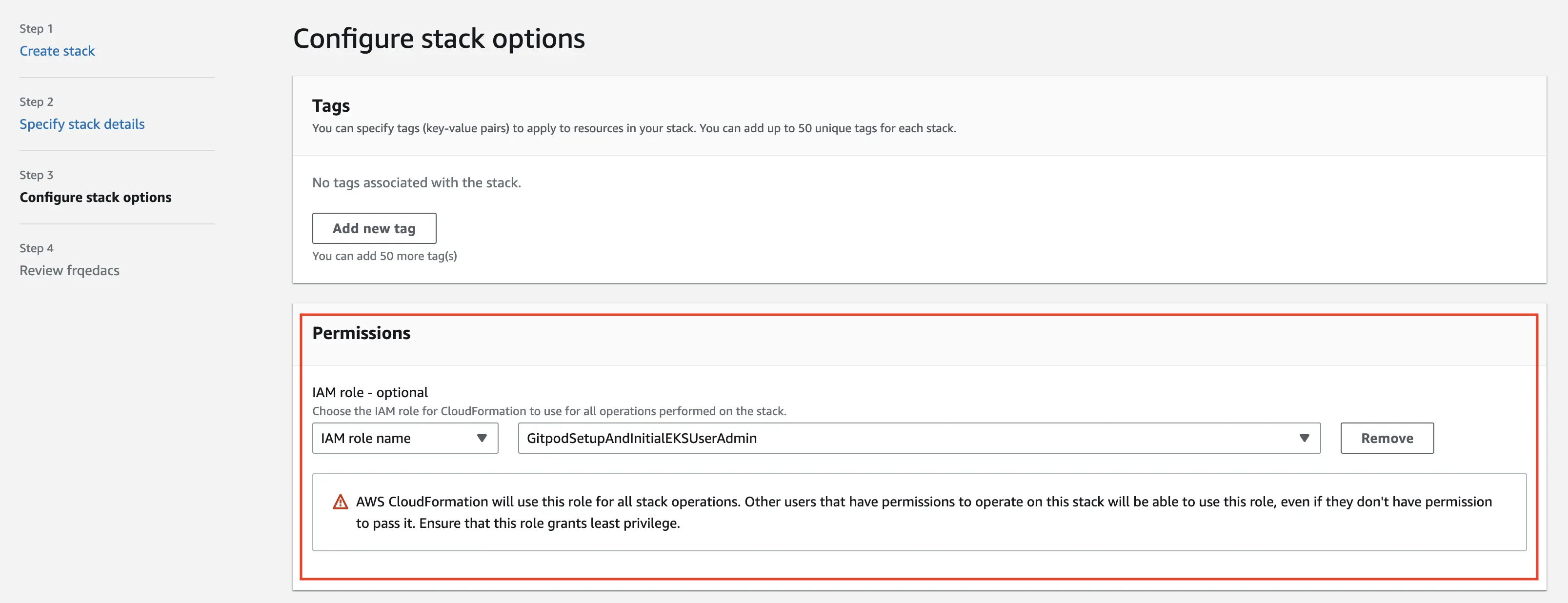
Important Message for Transit Gateway Users
Important Message for Transit Gateway Users
- Before executing the CloudFormation template, you need to ensure the Transit Gateway that the Gitpod instance attaches to is able to accept attachment requests. For this, the Transit Gateway needs to be shared using AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM) to allow for other AWS accounts in your Organization to send attachment requests for approval. More info on Transit Gateway attachments can be found in the AWS documentation.
- During the execution of the CloudFormation template, a Transit Gateway attachment to the Transit Gateway defined above is initiated. If you do not have resource sharing policies for this or auto accept turned on, you will have to manually accept this attachment request.
- The flow to manually approve the attachment request is as follows: Navigate to the AWS account the Transit Gateway attachment is in and navigate to the Transit Gateway Attachments page. Within 5 minutes of starting the CloudFormation execution, you should see a pending attachment in which you have limited time to approve else stack creation fails. Find out more in the AWS documentation.
- If you run into errors during the Cloudformation deployment you should remove all existing resources before trying again. There are a few resources that need to be cleaned up manually before you attempt another installation. See Deleting your Gitpod installation for details.
- Instance will install Gitpod: After the infrastructure has been created, the instance will register itself with the Enterprise Control plane. It will then ask for the newest version of Gitpod, and install it onto the created infrastructure.
3. Set Up Gitpod
Gitpod is now ready to be setup. Your Gitpod account manager will provide the URL to access it. This URL will contain a one time admin password. This is used to authenticate when no Single Sign-On (SSO) has been set up yet. You are three steps away from launching your first Gitpod workspace:Name your organization
Name your organization
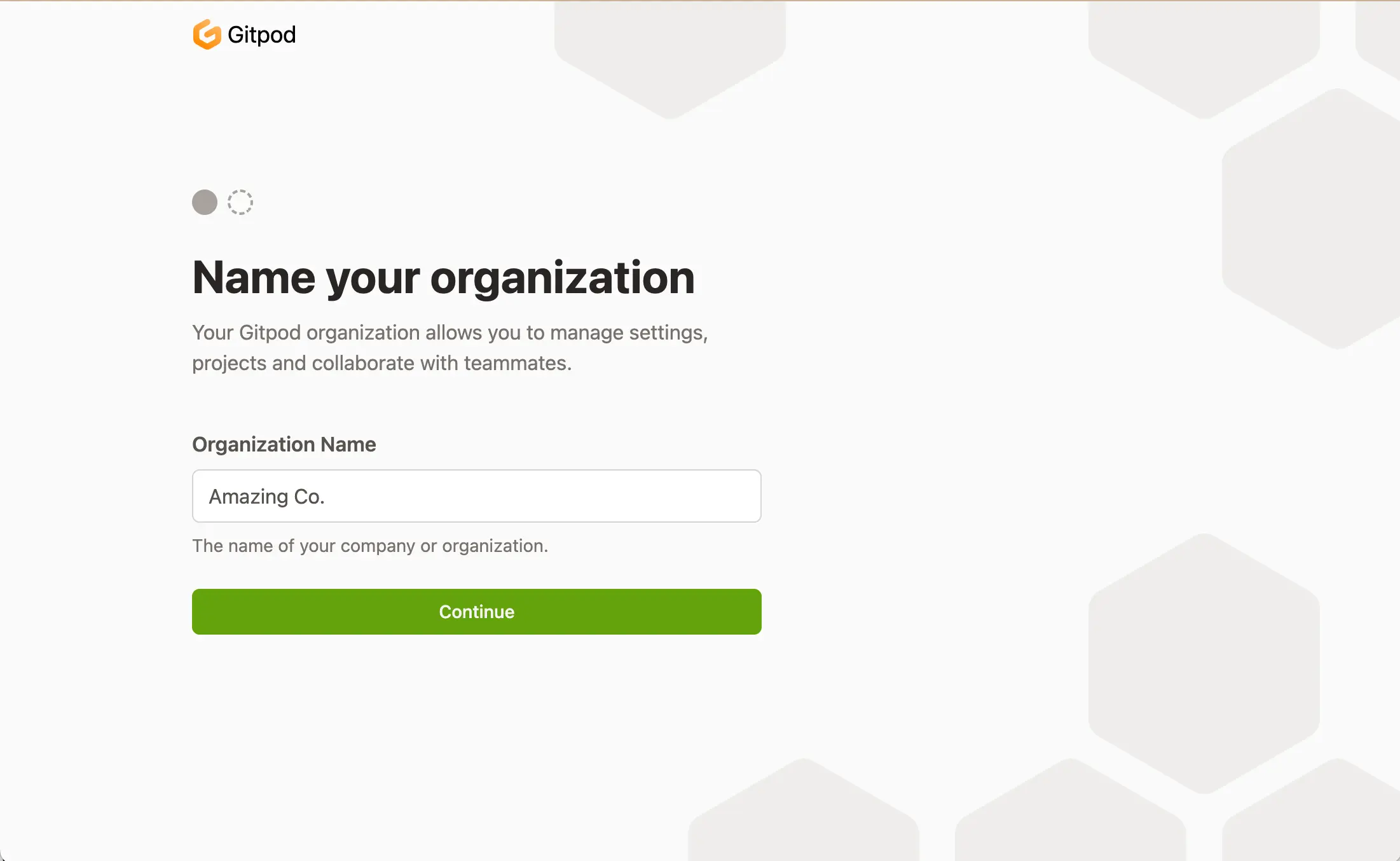
Name your organization

Preview in Gitpod Dashboard
Configure Single Sign-On
Configure Single Sign-On
- You will need to create a configuration with your Identity Provider and provide the “redirect URI” you can copy from this screen.
- Once you’ve created your Identity Provider configuration, you should copy and paste the Issuer URL, Client ID and Client Secret values on this screen.
-
Clicking “Verify SSO Configuration” will ensure that validity of the values by authenticating your account. If successful, your user will be created and configured with the “owner” role. Subsequent users that log in will be granted the default “member” role.
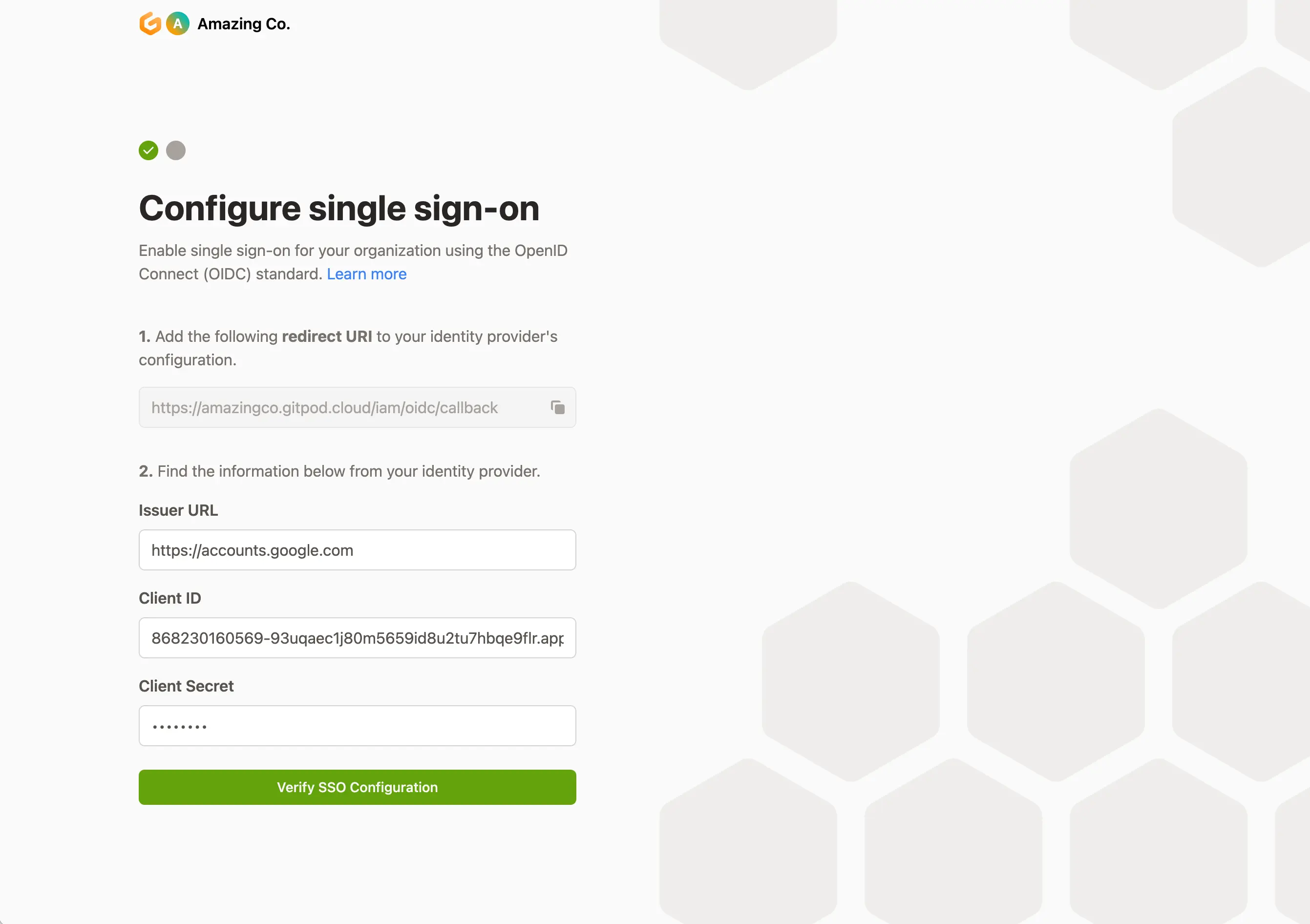
Configure Single Sign-on
Okta
Okta
- Access to your Okta instance
- Permission to create an app integration
- On the Okta Admin dashboard, navigate to Applications
-
Select
Create App Integration
Applications - Okta Dashboard
-
Select the following options and click
Next- Sign-in method:
OIDC - Open ID Connect - Application type:
Web Application
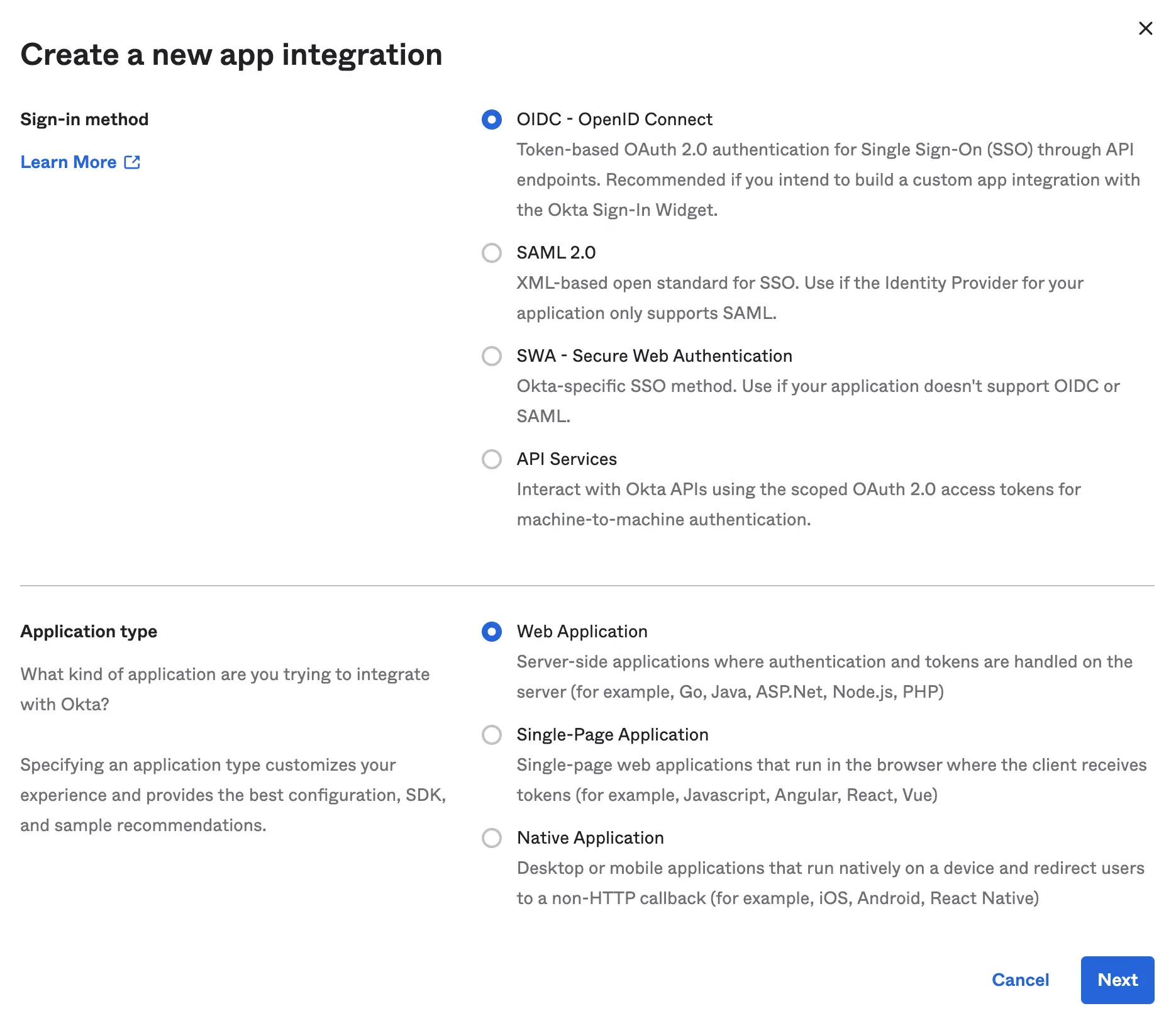
Create App Integration - Okta Dashboard
- Sign-in method:
-
Specify General Settings
- App integration name:
Gitpod(or choose your own name) - Sign-in redirect URIs: copy this value from your Gitpod setup screen (see details above under “General instructions”)
- Sign-out redirect URIs:
none - Trusted Origins:
none - Assignments: choose option appropriate to your organization
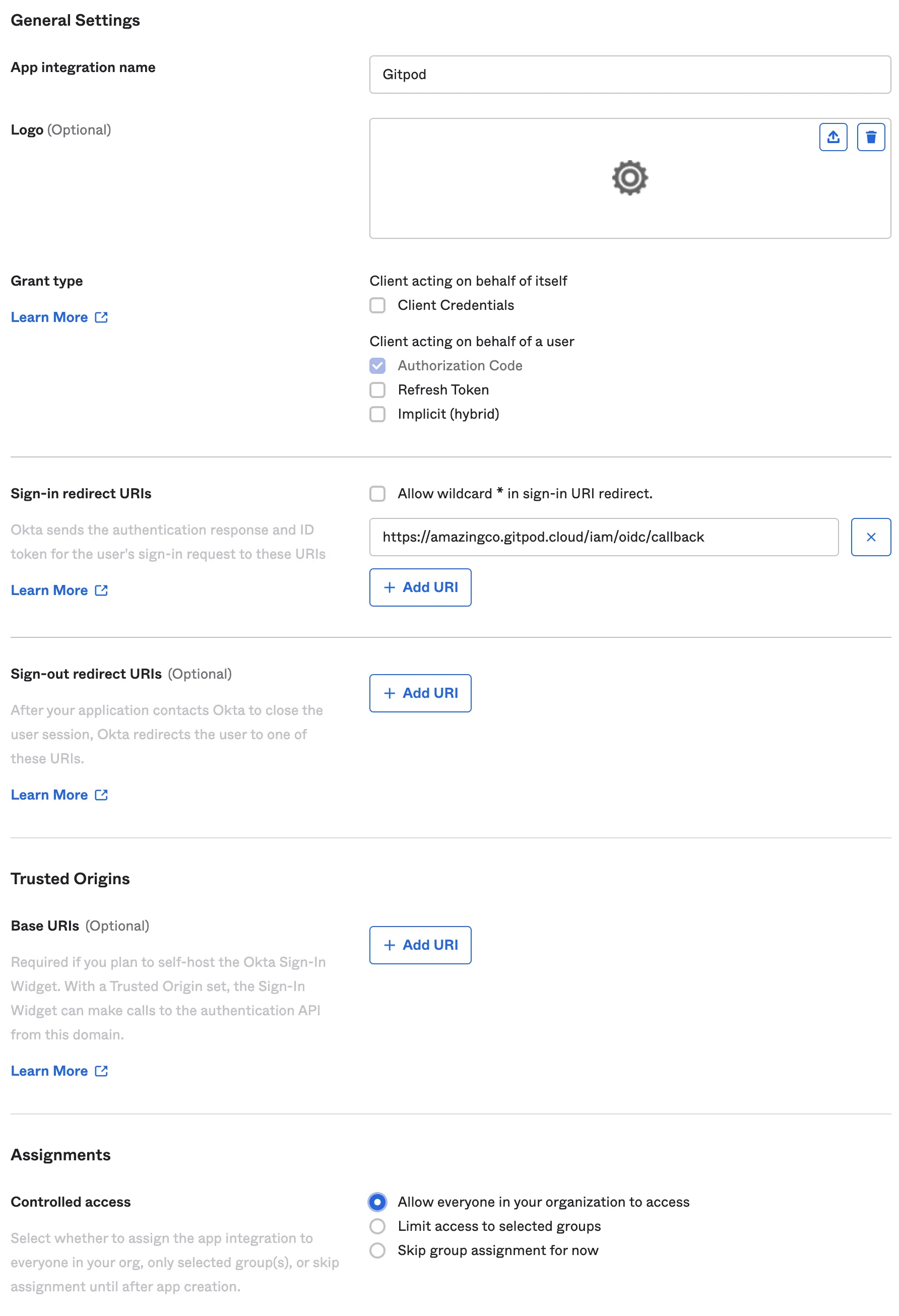
Specify Okta settings - Okta Dashboard
- App integration name:
-
Obtain Client ID & Client Secret
- Copy the
Client IDand use it as input in Gitpod setup (see details above under “General instructions”) - Copy
Client Secretand use it as input in Gitpod setup (see details above under “General instructions”) - Set the
Issuerto your Okta instance, eg:https://amazingco.okta.com/
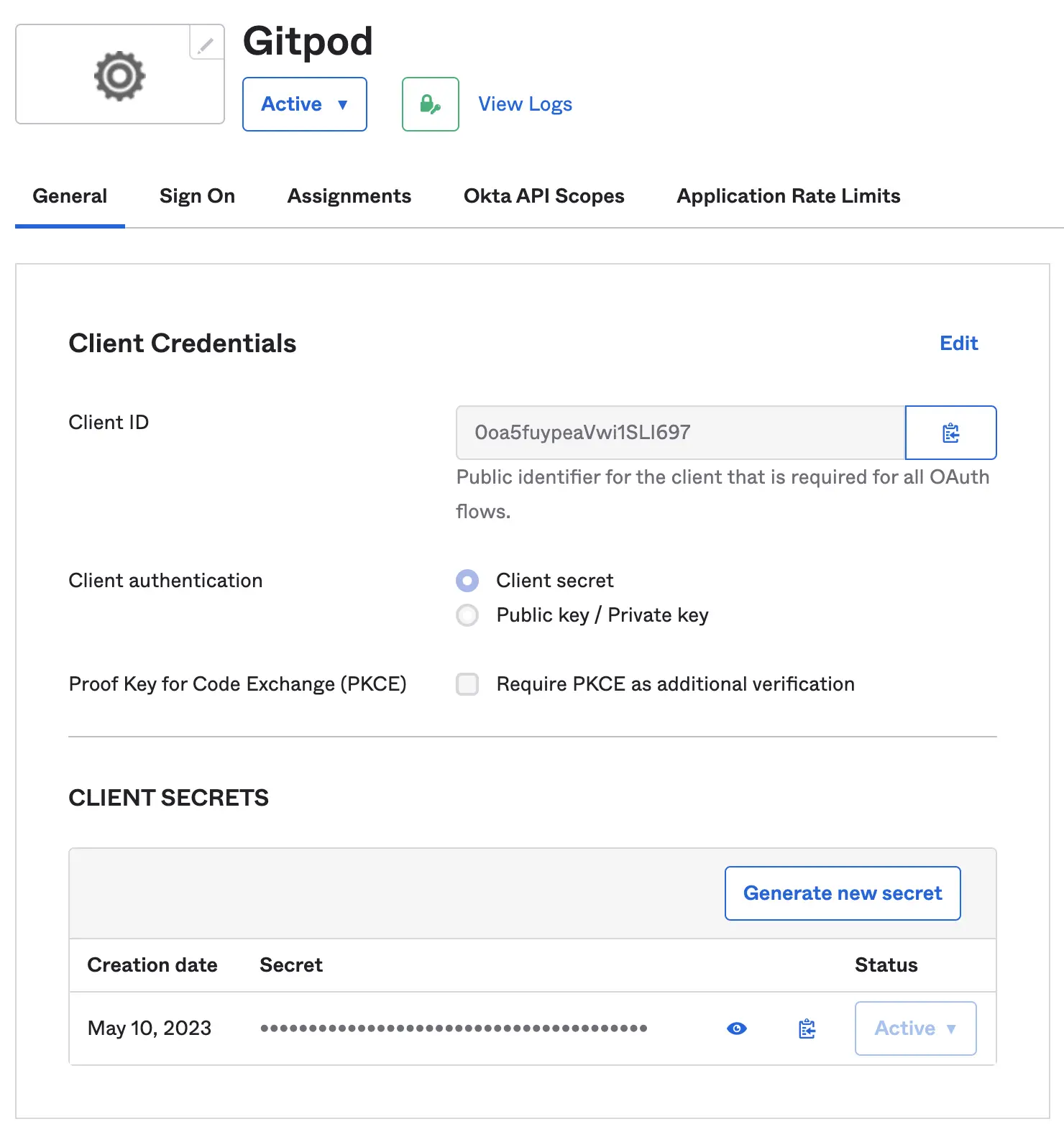
Configure Client Secrets - Okta Dashboard
- Copy the
- Continue with Gitpod SSO Configuration verification: Clicking “Verify SSO Configuration”
Google
- Access to setup a new API Credentials in your GCP Account
- Navigate to your Google Cloud Console, API Credentials
-
Select Create Credentials, and choose OAuth client ID
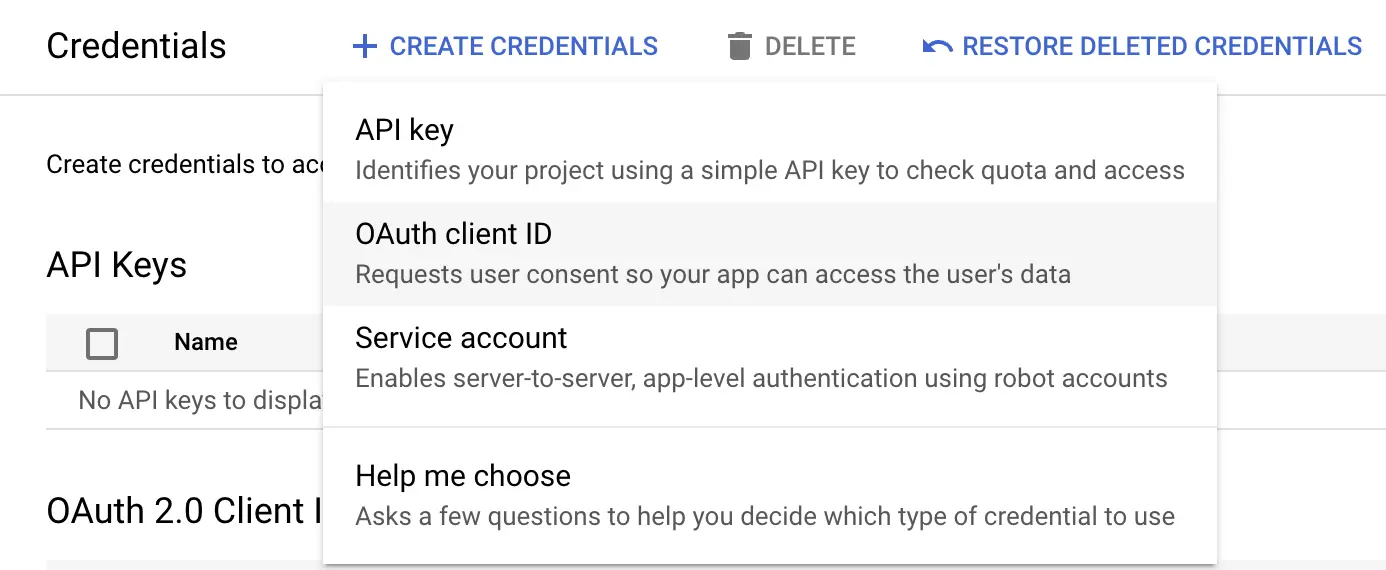
Create credentials - Google Cloud Dashboard
- Configure your OAuth Client ID, by specifying the Authorized Redirect URIs: Once you’ve created your Identity Provider configuration, you should copy…
-
Obtain the Client ID & Client Secret and input these into your Gitpod Setup page
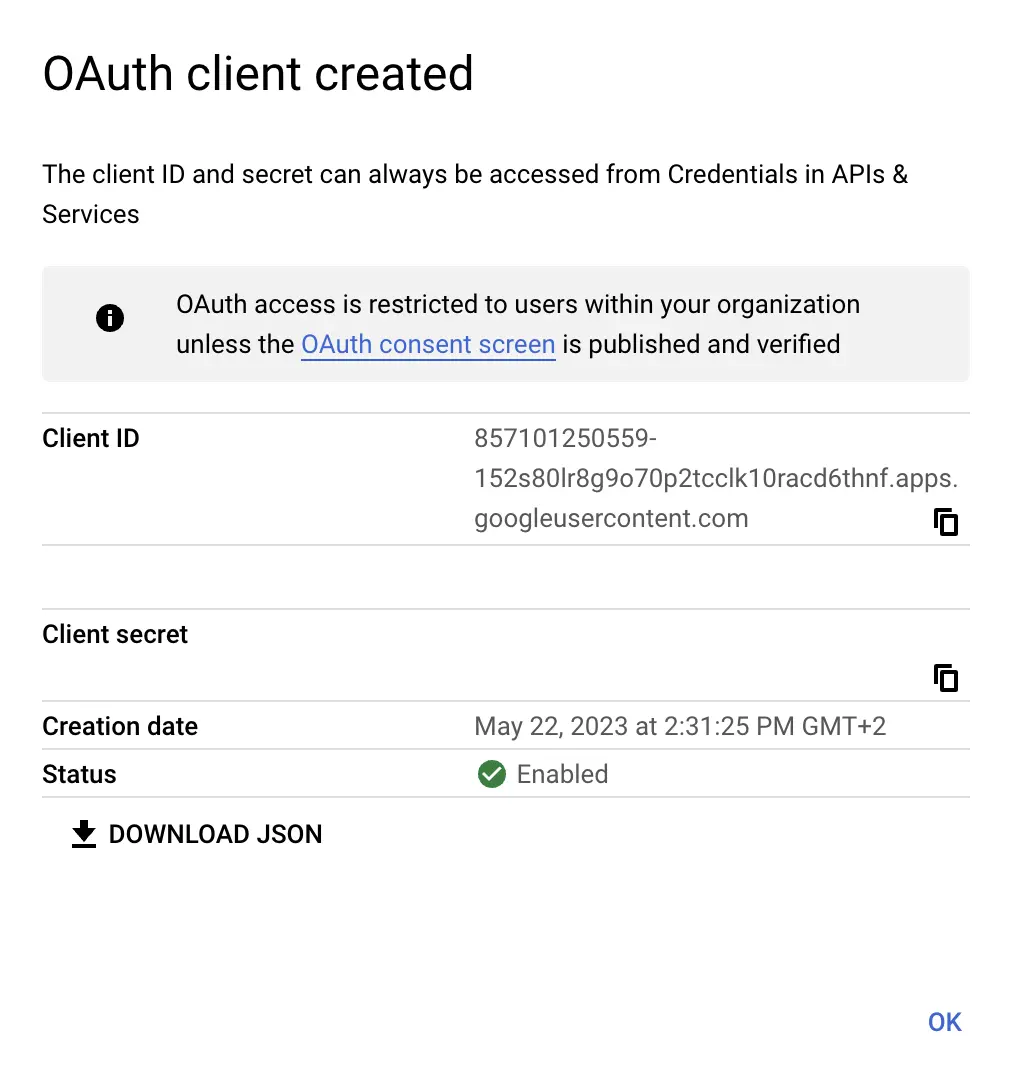
OAuth Client Created - Google Cloud Dashboard
-
Set Provider’s Issuer URL to
https://accounts.google.com - Proceed to verify the integration on the Gitpod setup page: Clicking “Verify SSO Configuration”
Azure AD
Azure AD
- Access to Azure Directory, to Register an Application
- Navigate to your Azure portal > App Registrations
-
Select New Registration
New registration - Azure AD Dashboard
- Name your application - e.g. Gitpod
- Select supported account types depending on your organizational needs. Most likely you want Accounts in this organizational directory only
-
Copy the redirect URL from the Gitpod SSO setup page and set it as the Redirect URI, selecting Web as the application type
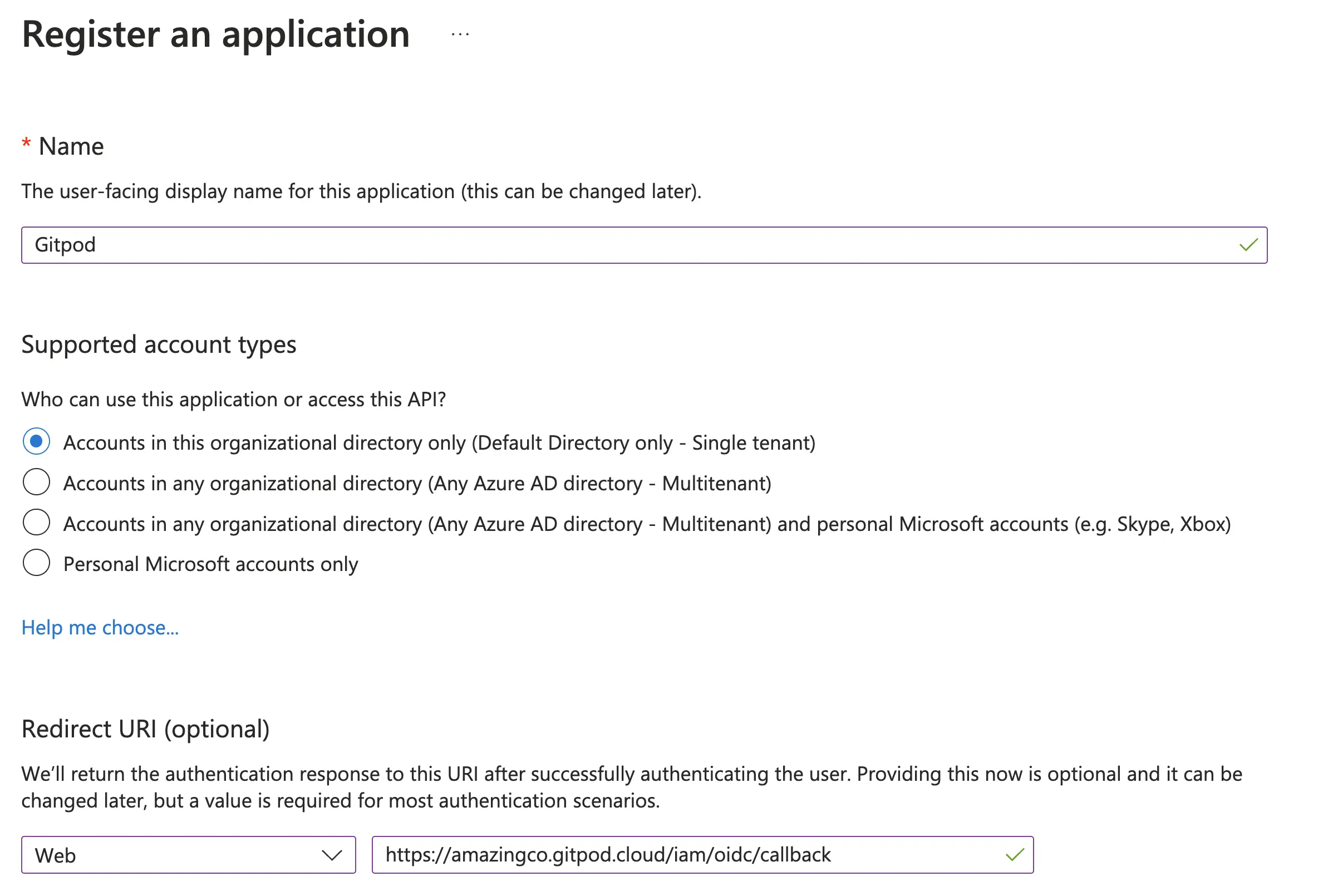
Register Application - Azure AD Dashboard
- From the App Registration Overview, you should obtain the Application (client) ID and copy it into your Gitpod SSO setup page
-
Create a client secret - navigate to Certificates & Secrets, click New client secret
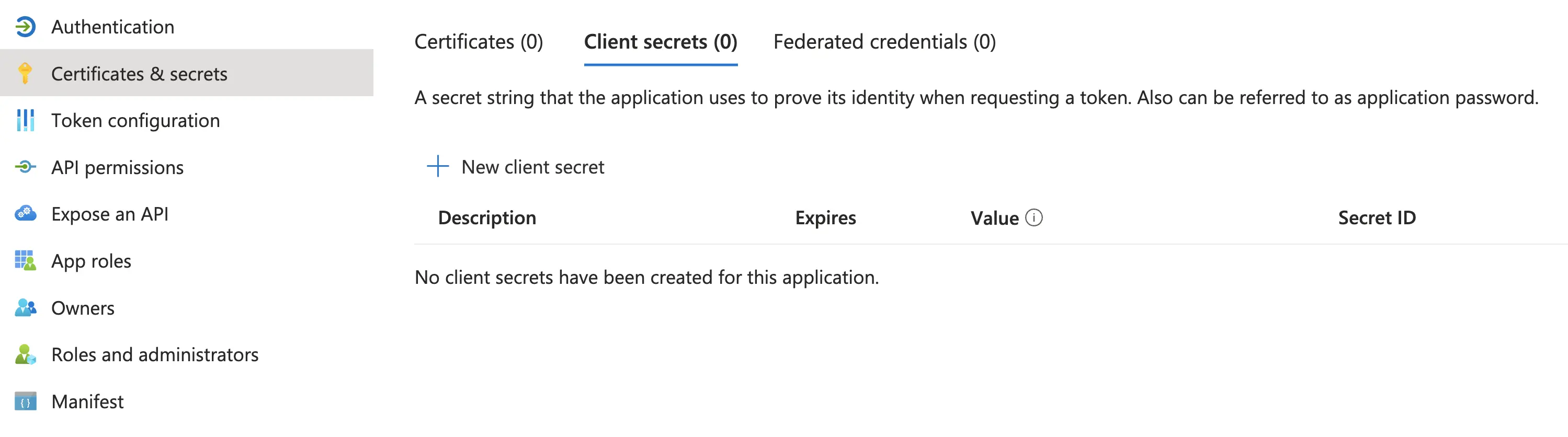
Create client secret - Azure AD Dashboard
-
Name the secret, and set expiry according to your needs.
📌 Once the client secret expires, you (nor anyone else in your organization) will be able to log in to Gitpod. You will need to update the SSO configuration (secret) to continue using SSO.
- Obtain the Secret Value and copy into into the Gitpod SSO Client Secret input field
-
Grant the application access to OpenId
email,openidandprofileinformation- Navigate to API Permissions
- Select Microsoft Graph
- Enable
OpenId.email,OpenId.openidandOpenid.profile
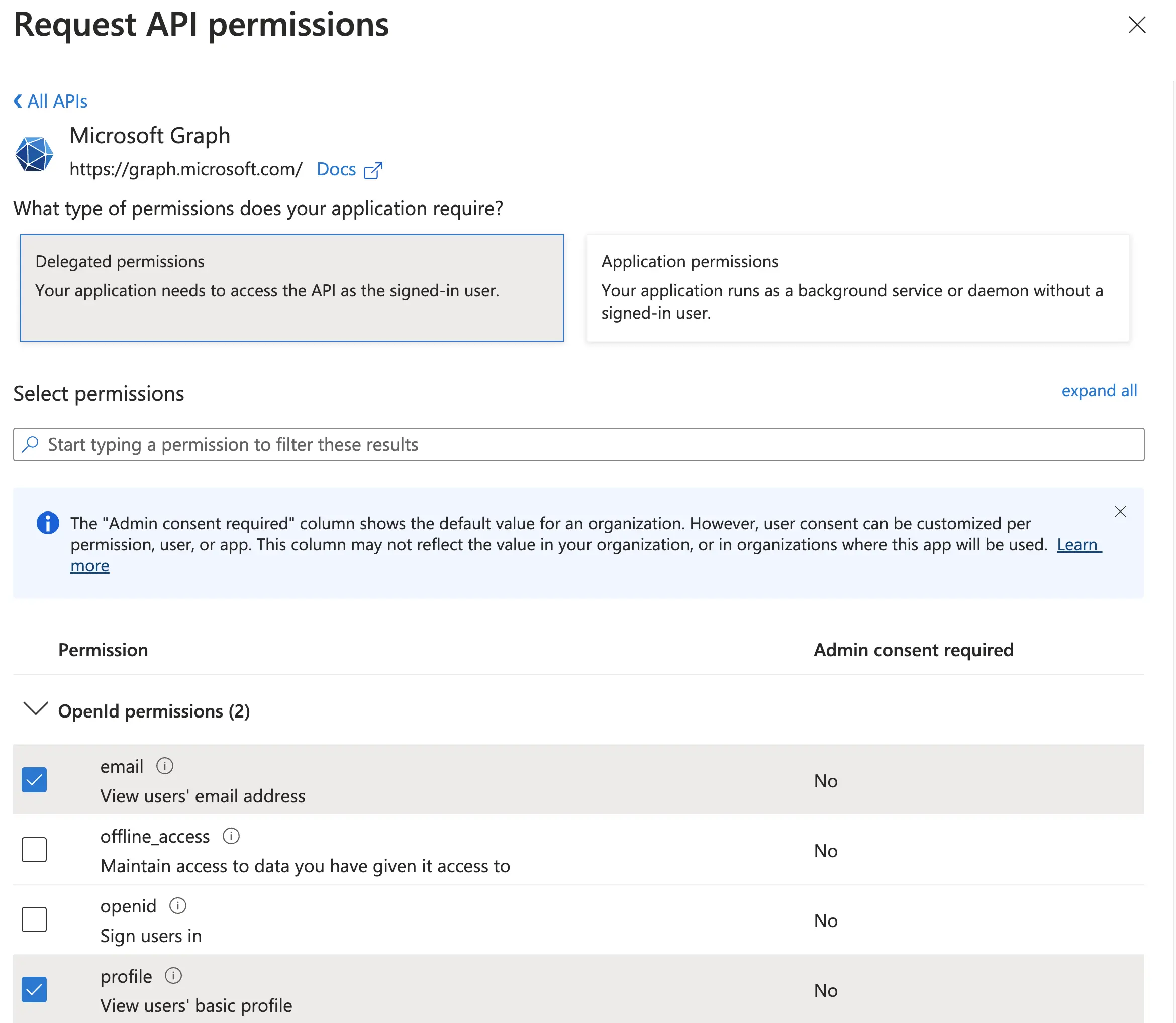
Request API Permissions - Azure AD Dashboard
- Once saved, your configured permissions should look as follows:
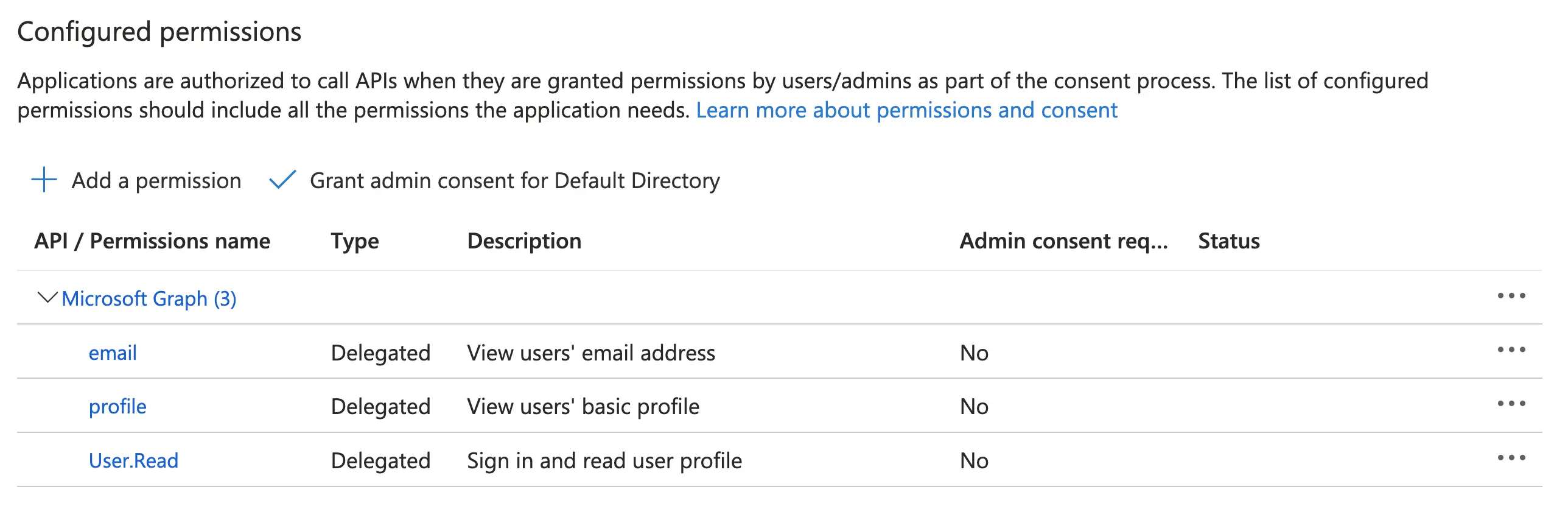
Configure API Permissions - Azure AD Dashboard
-
Obtain the Provider URL
- Navigate to your App Registration > Overview
- Click endpoints
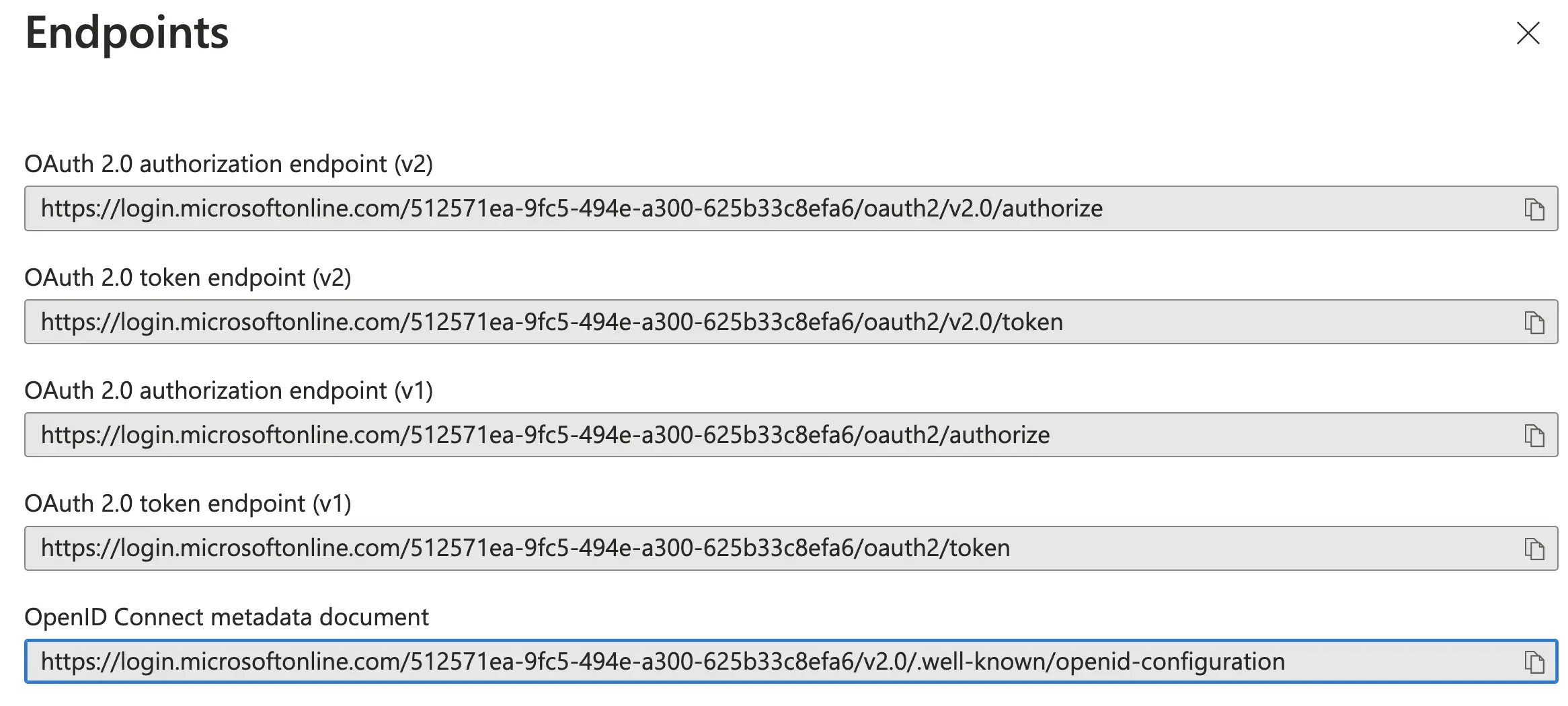
Endpoints - Azure AD Dashboard
- Find the entry for
OpenID Connect metadata document - Use the URL before the
.well-known/openid-configurationsegment,- For example:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/512571ea-9fc5-494e-a300-625b33c8efa6/v2.0/
- For example:
- Proceed to Verify the SSO configuration on the GitHub SSO setup page: : Clicking “Verify SSO Configuration”
AWS Cognito
AWS Cognito
- Navigate to the Cognito page in the AWS console. Select create user pool:
Congiton User Pool Process
- Configure sign-in experience:
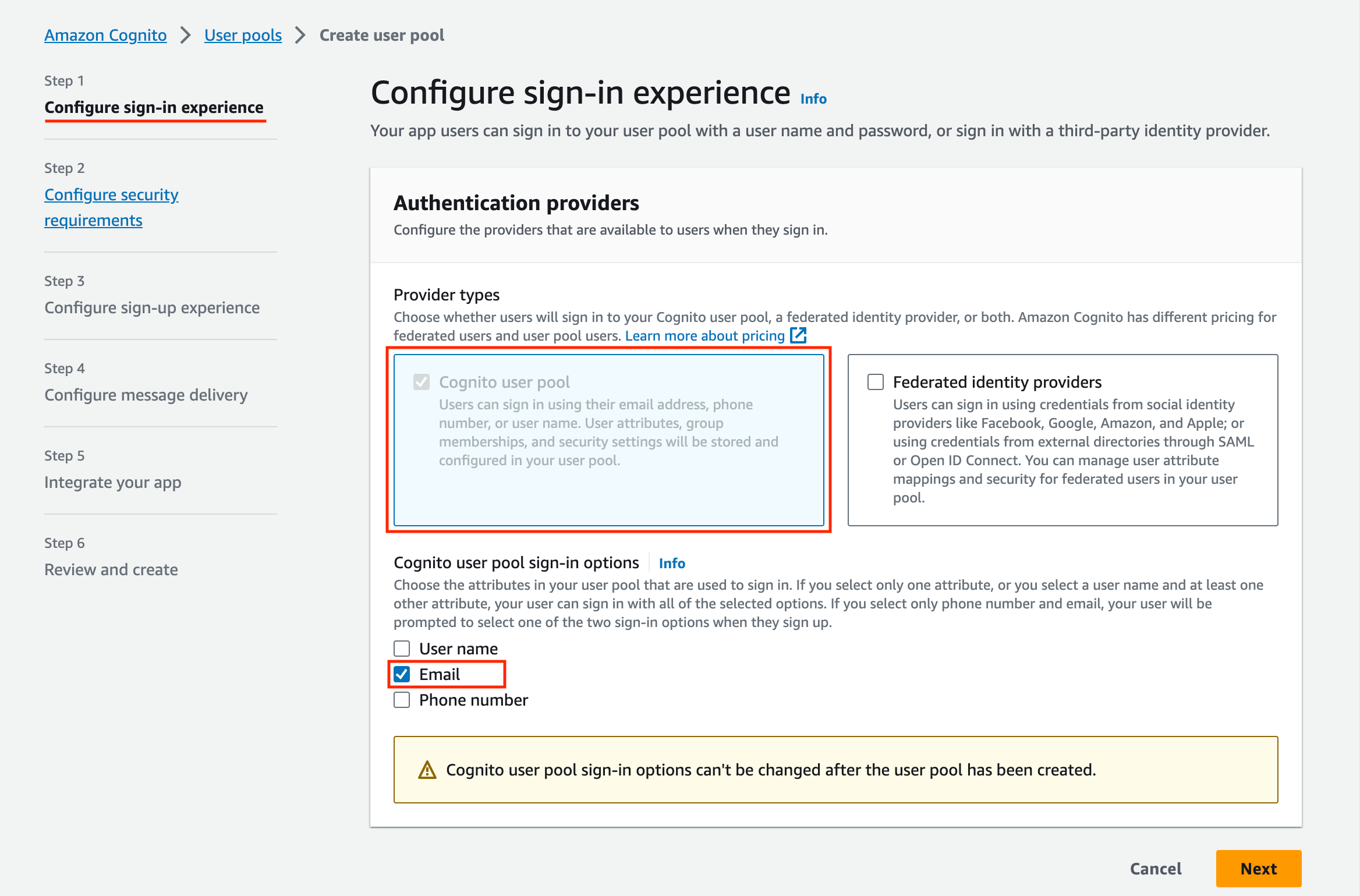
Congito Sing In Requirements
- Select
Cognito user poolas provider type - Select email as the Cognito user pool signin option
-
Configure Security requirements:
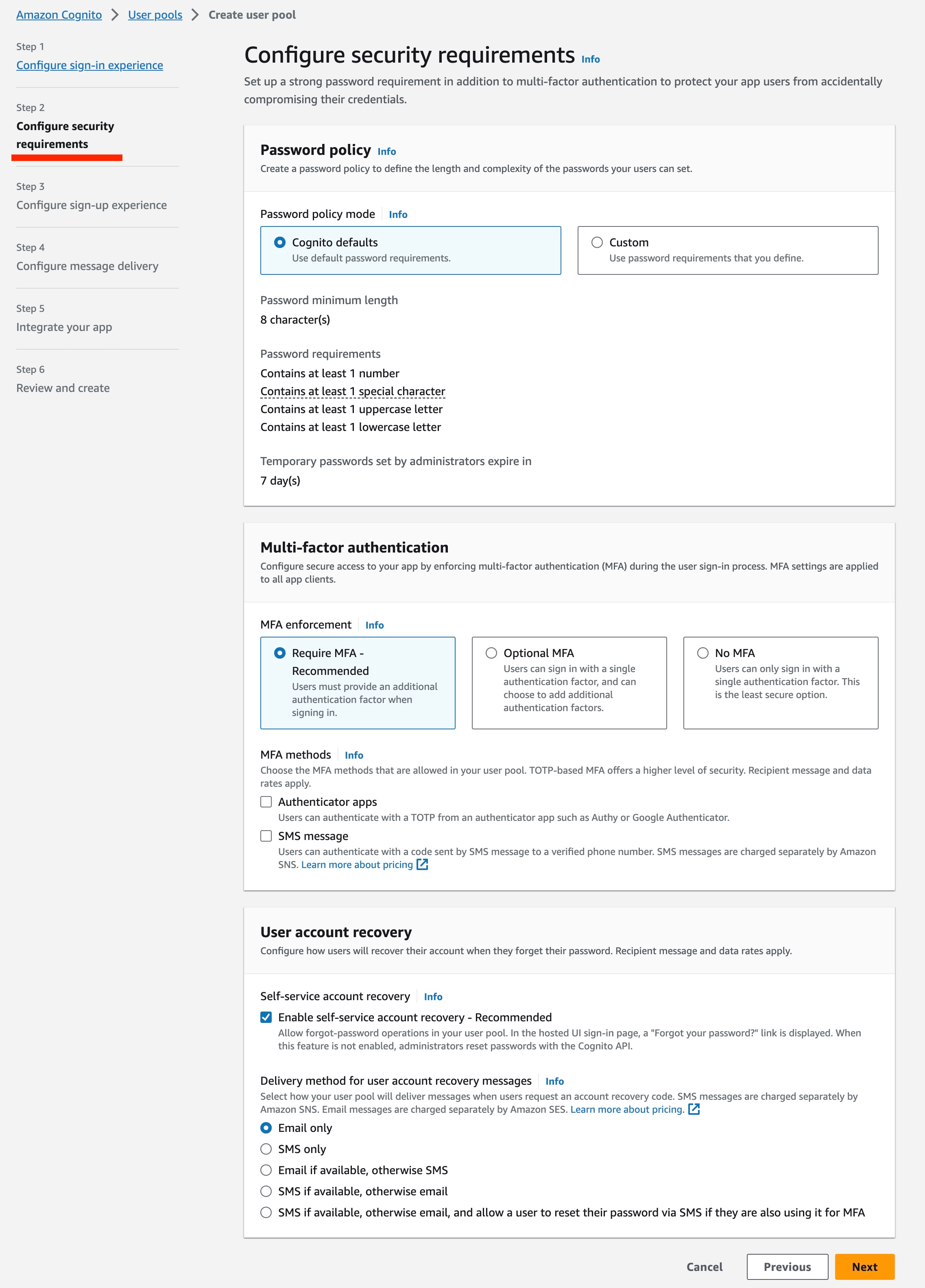
Congito Security Requirements
- For development purposes, consider modifying the MFA enforcment policy to not require MFA. For all production use cases, configure the MFA and user account recovery sections according to organizational guidelines
-
Configure sign-up experience:
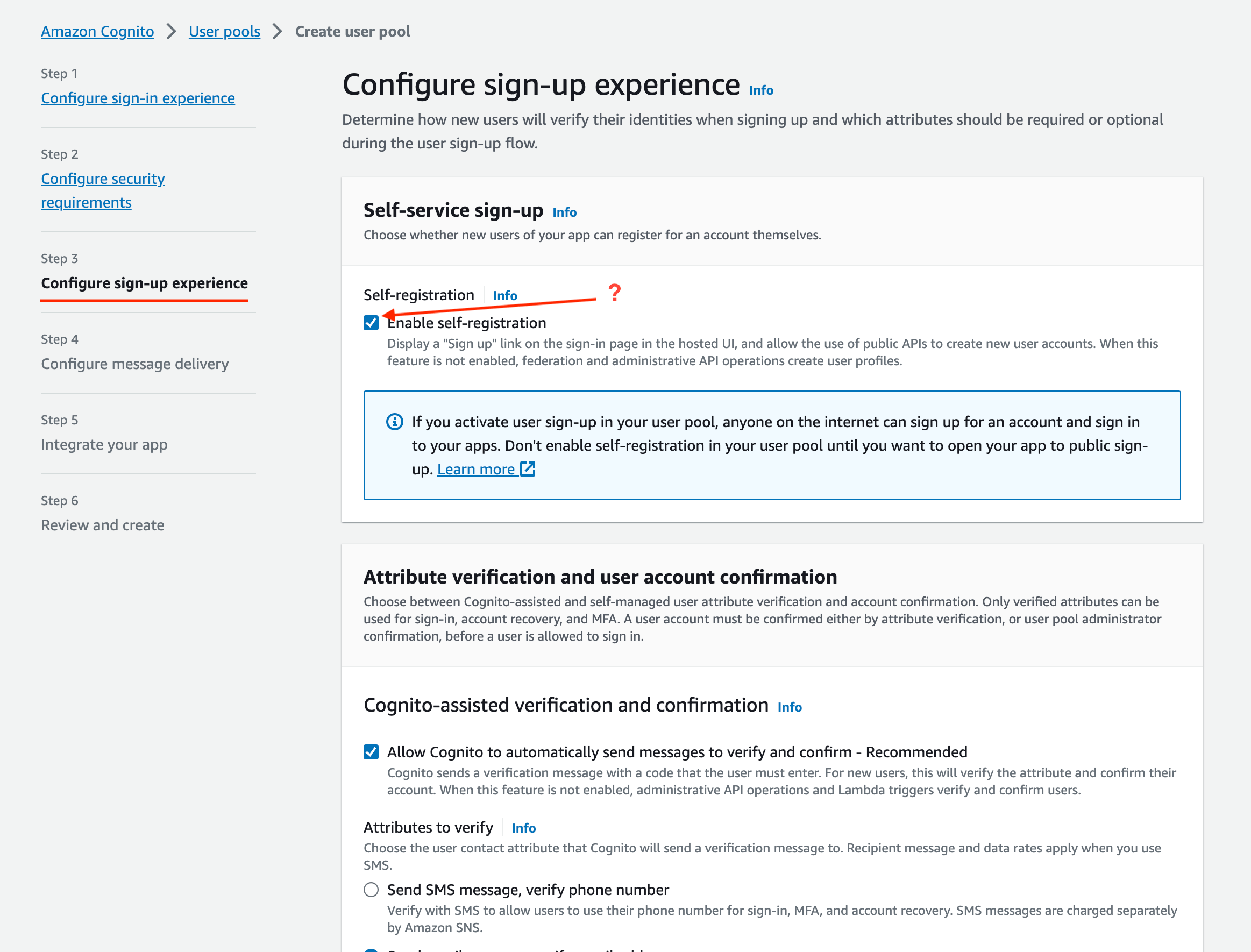
Congito Security Requirements
- Disable Self Registration if you want to limit access. For example, if your instance is accessible on the public internet, you may not want anyone to be able to self-register.
In theRequired Attributessection, ensure that name is selected: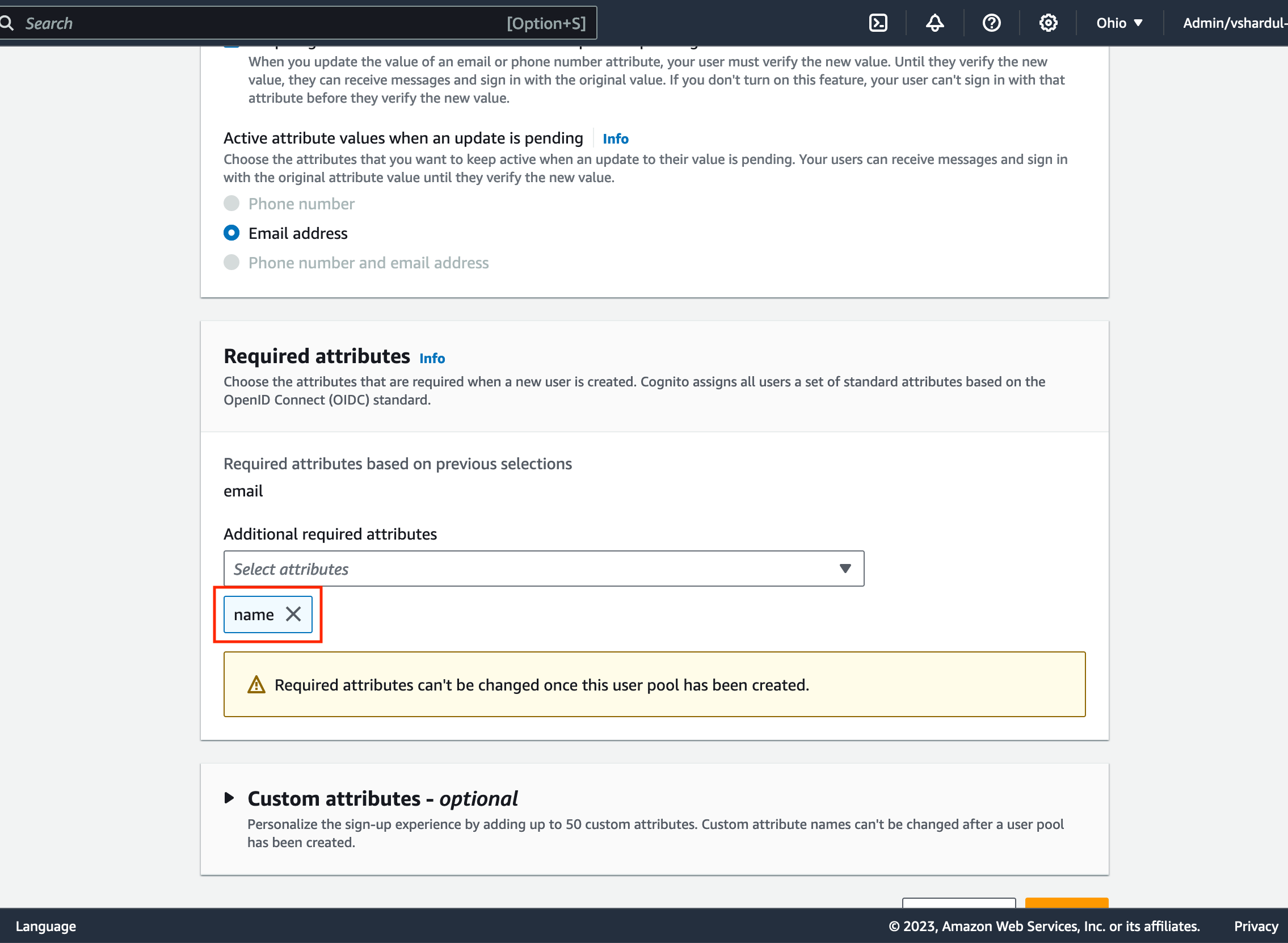
Required Attribute Name
-
Configure Message Delivery:
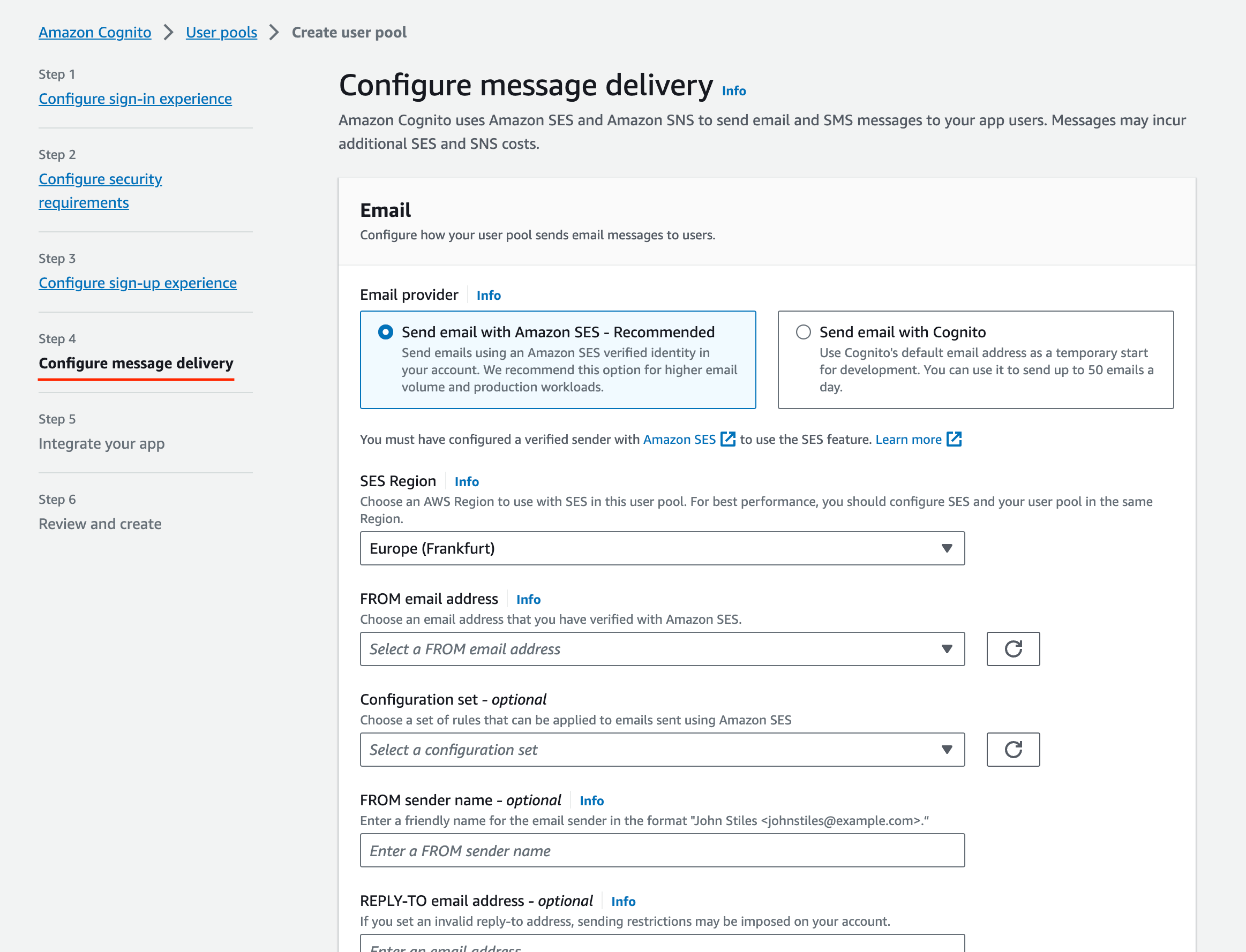
Configure message delivery
- For dev Setups, use Cognito as the email provider; for production setups, use company SES setup
-
Integrate your app:
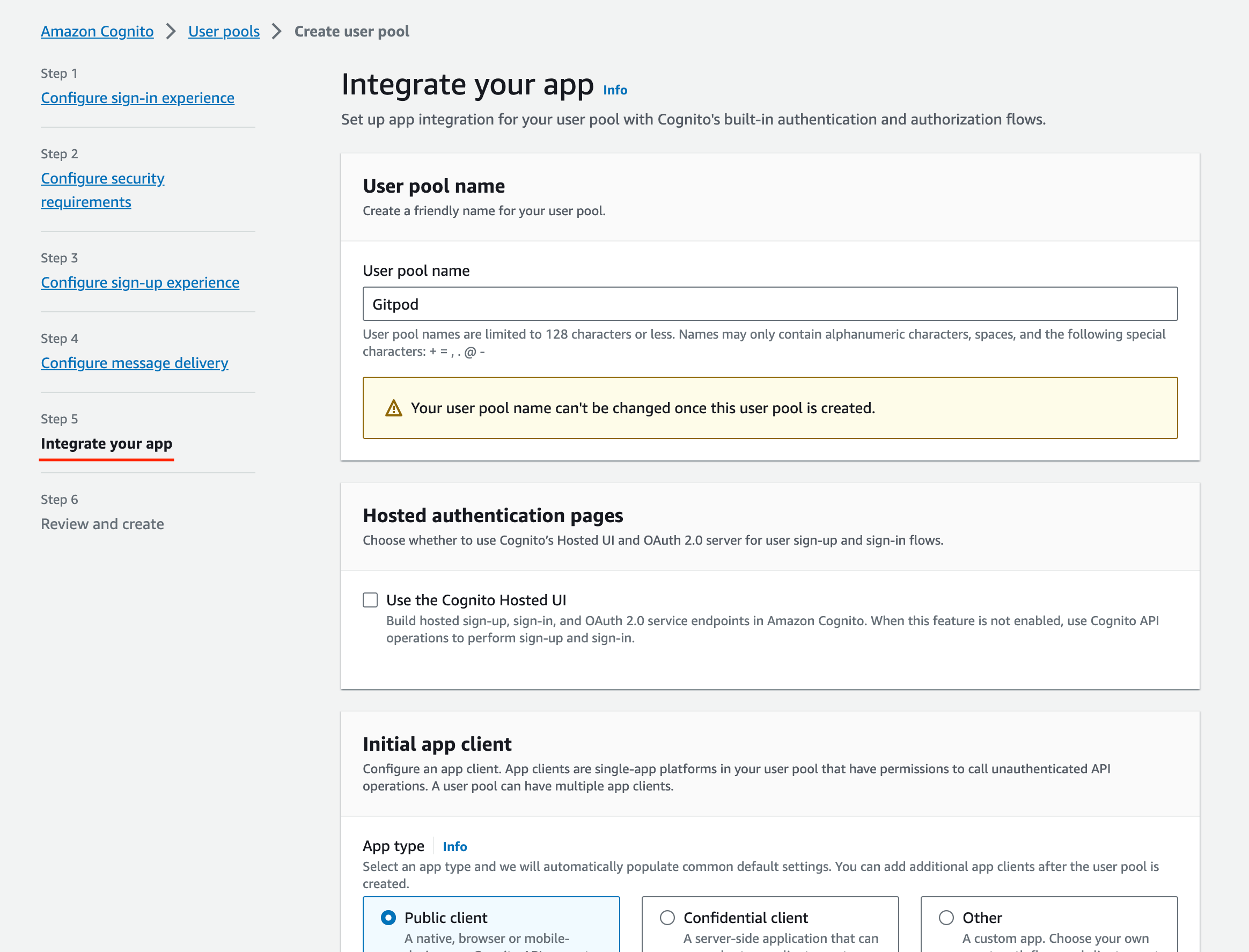
Integrate your app
- Follow company best practice for most settings - Ensure to select
Generate a client secretin the Client secret section:
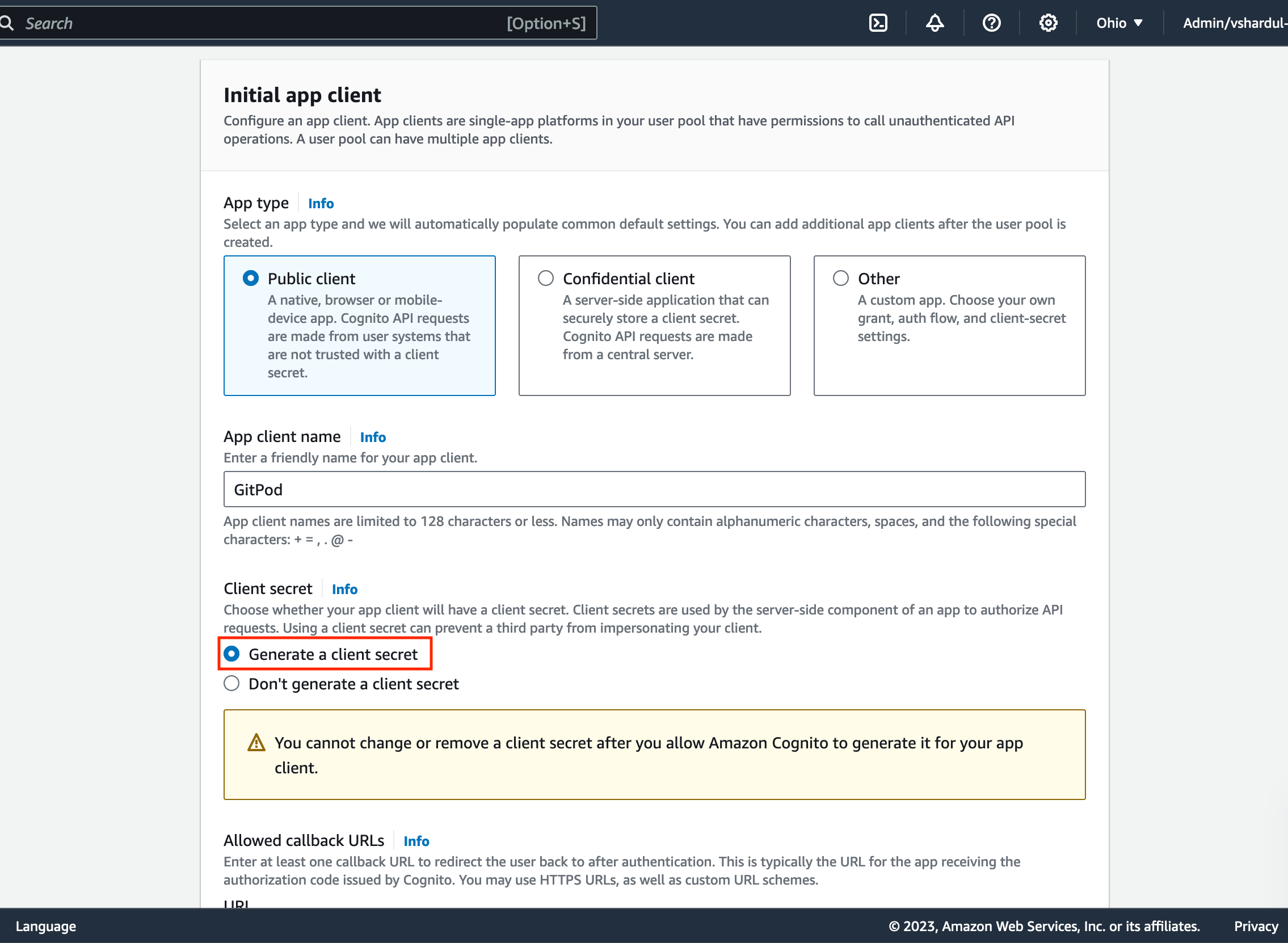
Required client secret
- Define the call back url as provided by the Enterprise instance in the Configure single sign-on setup page (see above):
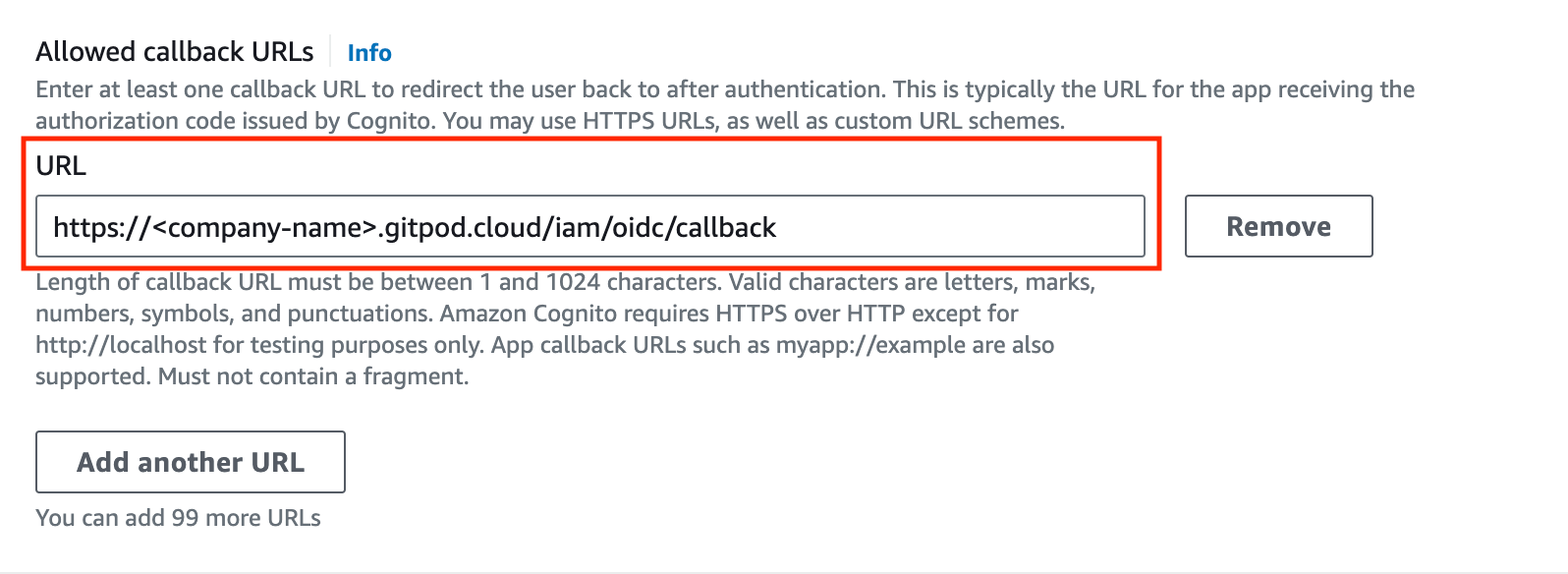
Required callback url
- As the identity provider, select
Cognito(under Advanced app client settings) - OAuth 2.0 grant types, selectAuth Code Grant- Under OpenID Connect Scopes, selectOpenID,Email,Profile:
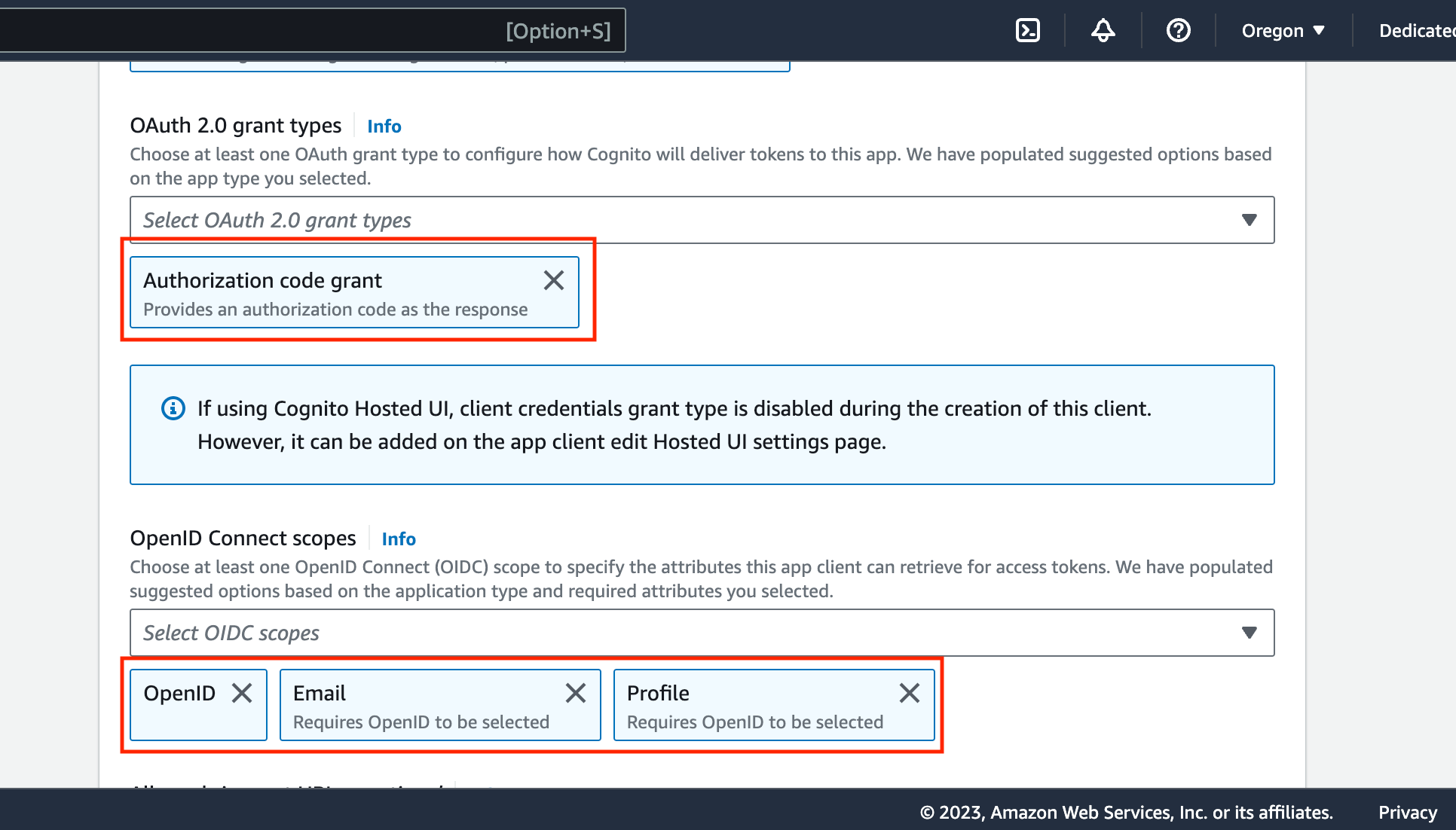
Required callback url
- Follow company best practice for most settings - Ensure to select
- Now create the cognito user pool. The review page should look similar to this:
- Start pasting the necessary values into the Gitpod SSO setup page. Navigate to:
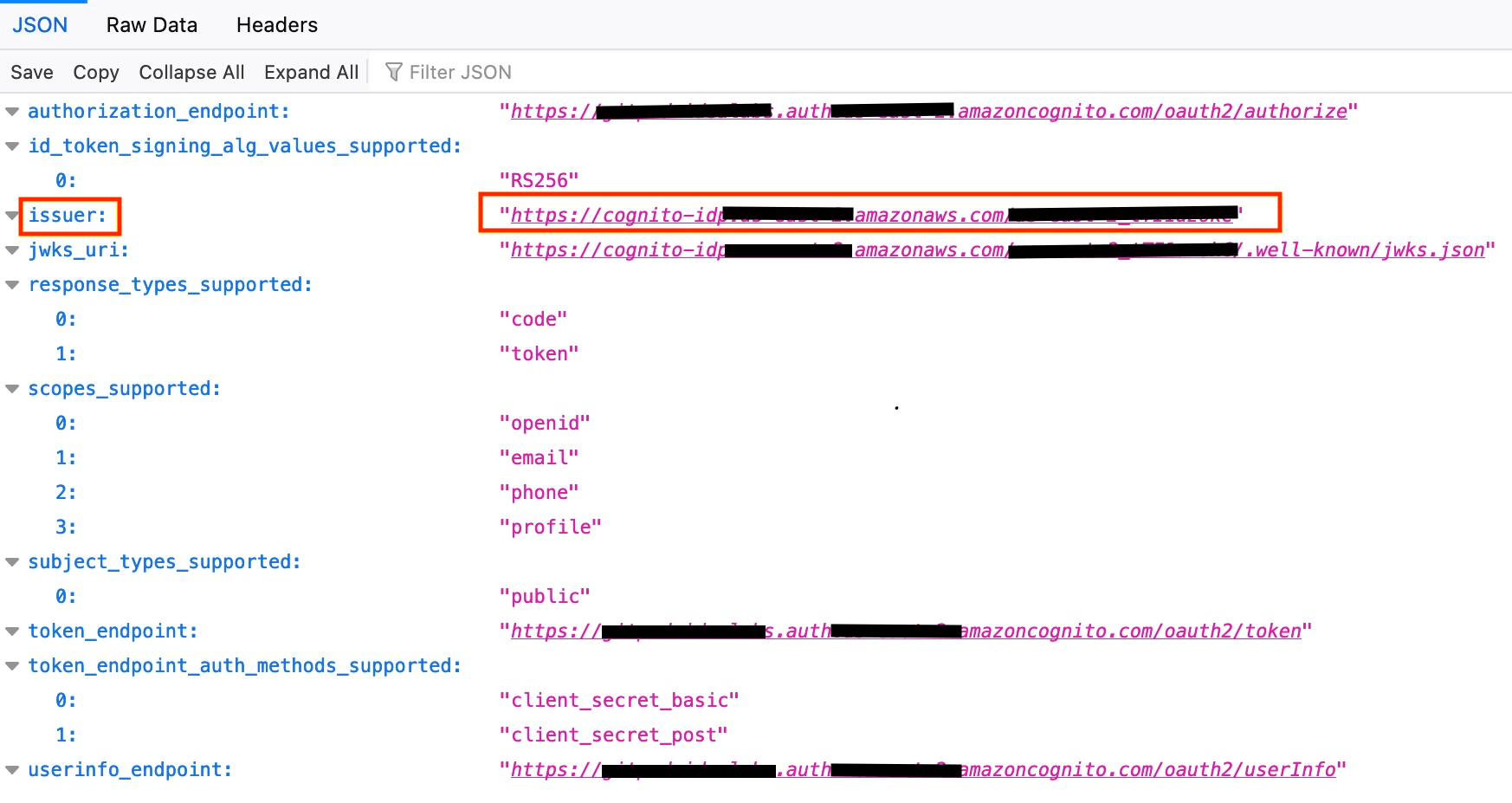
Issuer URL
- Copy the
issuer URLhighlighted above into the respective field on the Gitpod SSO setup page
- Navigate to the Cognito console, and find the User pool created above. Navigate to the App client meta data as below:
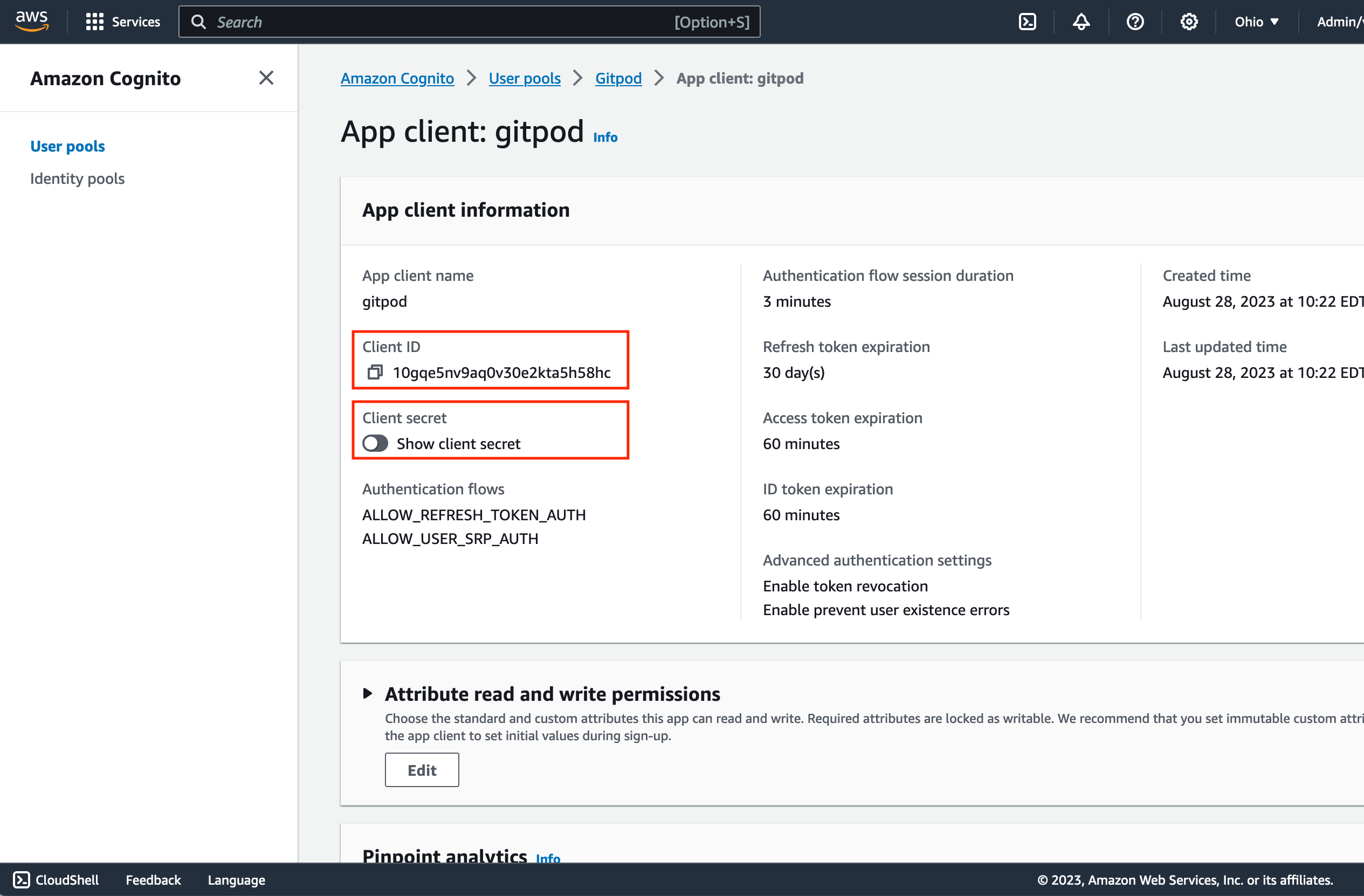
App Client Data
- Copy the
Client IDfrom the Cognito app client page into the respective field on the Gitpod SSO setup page - Copy the
Client Secretinto the respective field on the Gitpod SSO setup page
- Proceed to Verify the SSO configuration on the GitHub SSO setup page by clicking “Verify SSO Configuration”
Add an SCM integration for GitHub, GitLab or Bitbucket
Add an SCM integration for GitHub, GitLab or Bitbucket
- Look at these steps for information on how to integrate
GitLab.comwith your Gitpod instance. You will need to entergitlab.comas theProvider Host Namein the New Git Integration Modal if you want to use gitlab.com, contrary to what is described. - Look at these these steps for information on how to integrate
GitHub.comwith your Gitpod instance. You will need to entergithub.comas theProvider Host Namein the New Git Integration Modal if you want to use github.com, contrary to what is described. - Look at these steps for information on how to integrate
Bitbucket Serverwith your Gitpod instance. SelectBitbucket Serveras theProvider Typein the New Git Integration Modal. For bitbucket.org this requires configuring an “OAuth consumer” on a “workspace”. This is slightly different from the documented Bitbucket Server integration. See gitpod PR #9894 for an example.
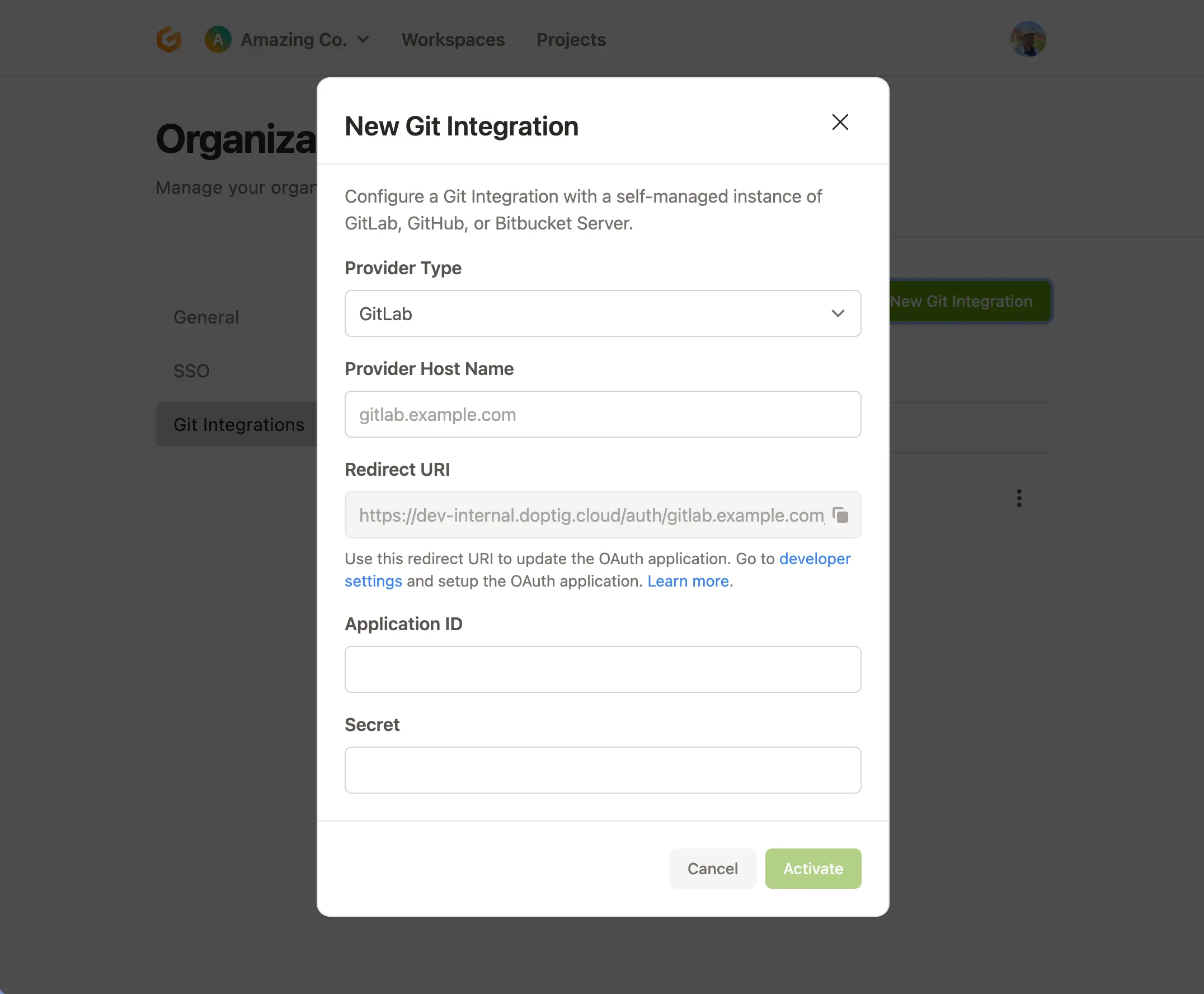
Git Integrations Preview in Gitpod Dashboard
4. Frequently Asked Questions
Click to view FAQ
Click to view FAQ
A. No. Enterprise is installed in a dedicated AWS account. This is to ensure that Enterprise can be installed without any conflicts with existing resources in your AWS account. If you have special requirements for the account please speak with your Gitpod account manager.Q. If we use the allPublic networking mode do we still need to provide a
CIDR range of our network?A. No. The
CIDR range of our network is only required when using the mixed or private networking modes.Q. If the Gitpod internal range of 100.70.0.0/16 does not need to be routable from my network, why do we need to specify the CIDR range of our network? A. User workspaces traffic must cross this range when reaching the rest of your network. If there are common internal services and systems that developers may need to access that overlap with this range, the experience may be inconsistent and difficult to troubleshoot. To avoid this, Gitpod can adapt the internally used CIDR range for workspaces to the customer’s CIDR range.Q. What if the
100.70.0.0/16 range overlaps with my network? A. Please contact your Gitpod account manager for assistance. There is some flexibility to the CIDR range used internally by Gitpod.Q. Why two templates?
A. The
gitpod-role CloudFormation template is used to create a role with the minimum permissions required to install and update Enterprise. This role and its policies are used to install the second Cloudformation template.Q. Can the stack created by gitpod-role be deleted after executing the <company>-gitpod-template.json? A. No, the stack created by
gitpod-role should be maintained. The role created is also used when updates are provided to the <company>-gitpod-template.json template. For more details on infrastructure updates, please see Deployment and Updates.Q. What happens if my Cloudformation stack fails to install?
A. If the stack fails to install, you should delete the stack and try again. There are a few resources that need to be cleaned up manually before you attempt another installation. See Deleting your Gitpod installation for details.Q. What if we want to use a custom domain name? A. Please see Using Custom Domains for more information about using a custom domain.Q. Can we grant public access to webhooks and IDP services without exposing the entire Gitpod application to the Internet?
A. Yes. Enterprise can be configured to expose webhooks and IDP services on public endpoints. This can be helpful for connecting to OIDC providers such as Okta, Azure AD. This option also makes it easy for developers to connect to your instance without having to route through a VPN or transit gateway. See Networking and Data flows for more information.

