IDEs and Editors
Rider
Rider is currently in Beta. Gitpod
continues to collaborate with
JetBrains · Send
feedback.
Getting started
- Install JetBrains Gateway - With the JetBrains Gateway and Gitpod plugin you can create and manage your latest 20 Gitpod workspaces.
- Install the Gitpod plugin - Open JetBrains Gateway and you’ll see the Gitpod logo on the main page. Click “install” to install the Gitpod plugin for JetBrains Gateway.
- Update your Gitpod preferences - Select Rider on the Gitpod preferences page which will set Rider as your default IDE for future workspace starts.
- Start (or restart) your workspace - Either start a workspace directly from within the JetBrains Gateway via the Gitpod plugin OR open a new workspace directly in Gitpod where on workspace start you will be prompted to open Rider for that workspace.
Updating Gitpod IDE preferences to Rider
Opening a JetBrains IDE from Gitpod
Updating the Gitpod plugin in JetBrains Gateway
Opening a JetBrains IDE from Gateway
Important: You must restart any started workspaces for your IDE
preferences to take effect.
Prerequisites
To successfully use Rider and load a .NET project, your workspace needs the .NET Framework or a compatible alternative, to be installed. The default workspace image does not come with .NET pre-installed, so you have two options: Using the .NET workspace image (Recommended)- Create a
.gitpod.ymlfile - Set the
imageproperty toimage: gitpod/workspace-dotnet:latestor alternatively, use a custom Dockerfile
- Using a workspace terminal, install
dotnetor a compatible alternative - Restart the IDE
Install Plugins
This section relates to plugin management when using JetBrains IDEs in a
remote development context. For information on regular plugin management,
refer toRider docs.
- Rider backend plugins - The JetBrains Rider backend runs within the remote Gitpod workspace. Backend plugins contribute functionality for IDE experiences relating to the filesystem, tools or languages and frameworks. When installed, a backend plugin only applies to the currently running Gitpod workspace and is not associated with a user. However, a plugin can be preconfigured for all users of a repository so that the plugin is enabled with every workspace start. It is not currently possible to install a backend plugin that applies to all workspaces of a Gitpod user or organization.
- JetBrains Client plugins - The JetBrains client runs on the users local machine and can be thought of as the user interface to the remote Rider backend. Client plugins are different to backend plugins as they contribute to the user interface aspect of the IDE experience (e.g. keyboard shortcuts and themes). Once installed, a client plugin is enabled for all Gitpod workspaces the user opens (if the workspace is running the exact same version of the Rider backend where the plugin was initially installed).
- JetBrains Gateway plugins - The JetBrains Gateway is an application downloaded onto a users local machine which allows users to start JetBrains Clients that are compatible with the Rider backend, running in a Gitpod workspace. JetBrains Gateway plugins are installed directly in JetBrains Gateway and contribute to remote development connection experiences (e.g. the Gitpod JetBrains Gateway plugin).
Install on JetBrains Client
The JetBrains client runs on the users local machine and can be thought of as the user interface to the remote Rider backend. Client plugins contribute to the user interface aspect of the IDE experience (e.g. keyboard shortcuts and themes). Once installed, a client plugin is enabled for all Gitpod workspaces the user opens (if the workspace is running the exact same version of the Rider backend where the plugin was initially installed). To install a plugin on JetBrains Client follow these steps:- In JetBrains Client open the IDE settings and select Plugins.
- Find the plugin in the Marketplace and click Install.
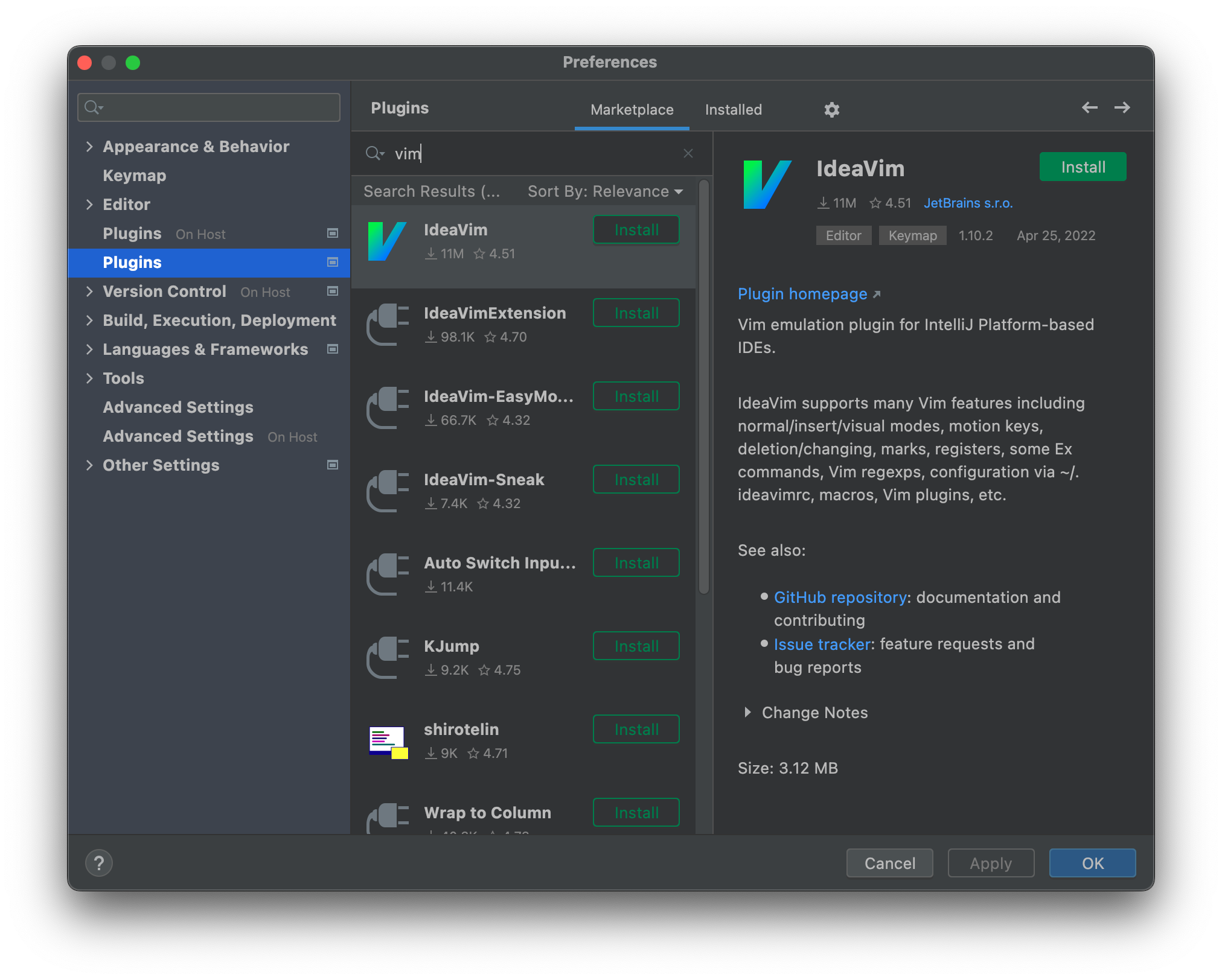
Install a plugin on JetBrains Client
Install on Rider backend
The JetBrains Rider backend runs within the remote Gitpod workspace. Backend plugins contribute functionality requiring access to IDE experiences such as the remote filesystem (e.g. contributing support of languages and frameworks). When installed, a backend plugin only applies to the currently running Gitpod workspace and is not associated with a user. However, a plugin can be preconfigured for all users of a repository so that the plugin is enabled with every workspace start. It is not currently possible to install a backend plugin that applies to all workspaces of a Gitpod user or organization.Install for your current workspace
You can install a plugin only for your current workspace following these steps:- In JetBrains Client open the IDE settings and select Plugins On Host.
- Find the plugin in the Marketplace and click Install.
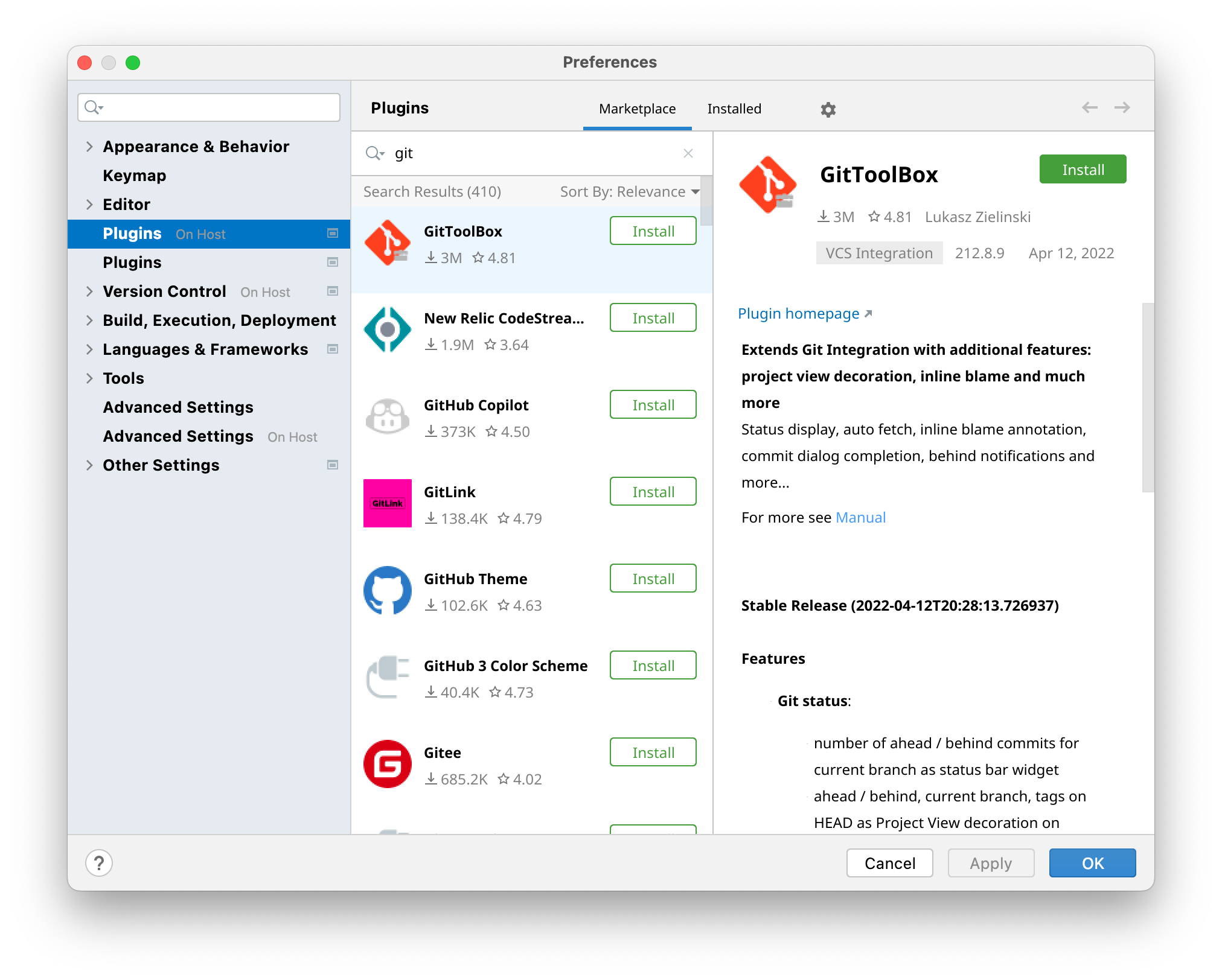
Install a plugin on Rider backend
Configure plugins for repository
You can share a plugin on Rider backend with everybody working on the repository by adding it to .gitpod.yml and pushing to your Git repository. Each workspace is preconfigured with plugins from thegitpod.yml configuration file. For example:
.gitpod.yml
Overview page of the specific plugin you’re interested in. The Plugin ID is usually found at the bottom of this page.
Configure custom plugin repositories
If you are using custom repositories, you can directly specify the URL of your custom repository or the identifier of your custom plugin. For example:.gitpod.yml
Install plugins from a workspace image
Within your Dockerfile for the workspace image, copy the plugin archive (.zip file) to one of the following directories:/home/gitpod/.gitpod/jetbrains/plugins- This location installs plugins to all JetBrains products (IntelliJ IDEA, GoLang, etc)./home/gitpod/.gitpod/jetbrains/rider/plugins- This location will install plugins only to the given IDE, e.g. Rider.
Before starting the Rider backend, Gitpod will read the locations specified
above and install plugins.
Install plugins per a user
To install plugins solely your user only profile, use the same approach as described in install from a workspace image. However, store your IDE Plugins in .dotfiles instead of the workspace image.Configure JVM options
Gitpod automatically sets the Java maximum memory heap size (
-Xmx) based
on workspace resources. You can override this default using any options
provided below.-Xmx memory size use .gitpod.yaml or set the env RIDER_VMOPTIONS via environment variables. For example:
.gitpod.yml
Configure IDE settings
Feedback needed: The below shows how you can configure global settings
with JetBrains. To leave feedback on the approach, please see this GitHub
issue: #6576. Also note
that JetBrains is working on comprehensive settings sync
functionality.
On JetBrains Client
IDE Settings that are configured on the JetBrains Client are stored on your local machine and don’t haveOn Host label in the IDE settings. These IDE settings are reused if the workspace is running the exact same version of the Rider backend where the settings were initially configured.
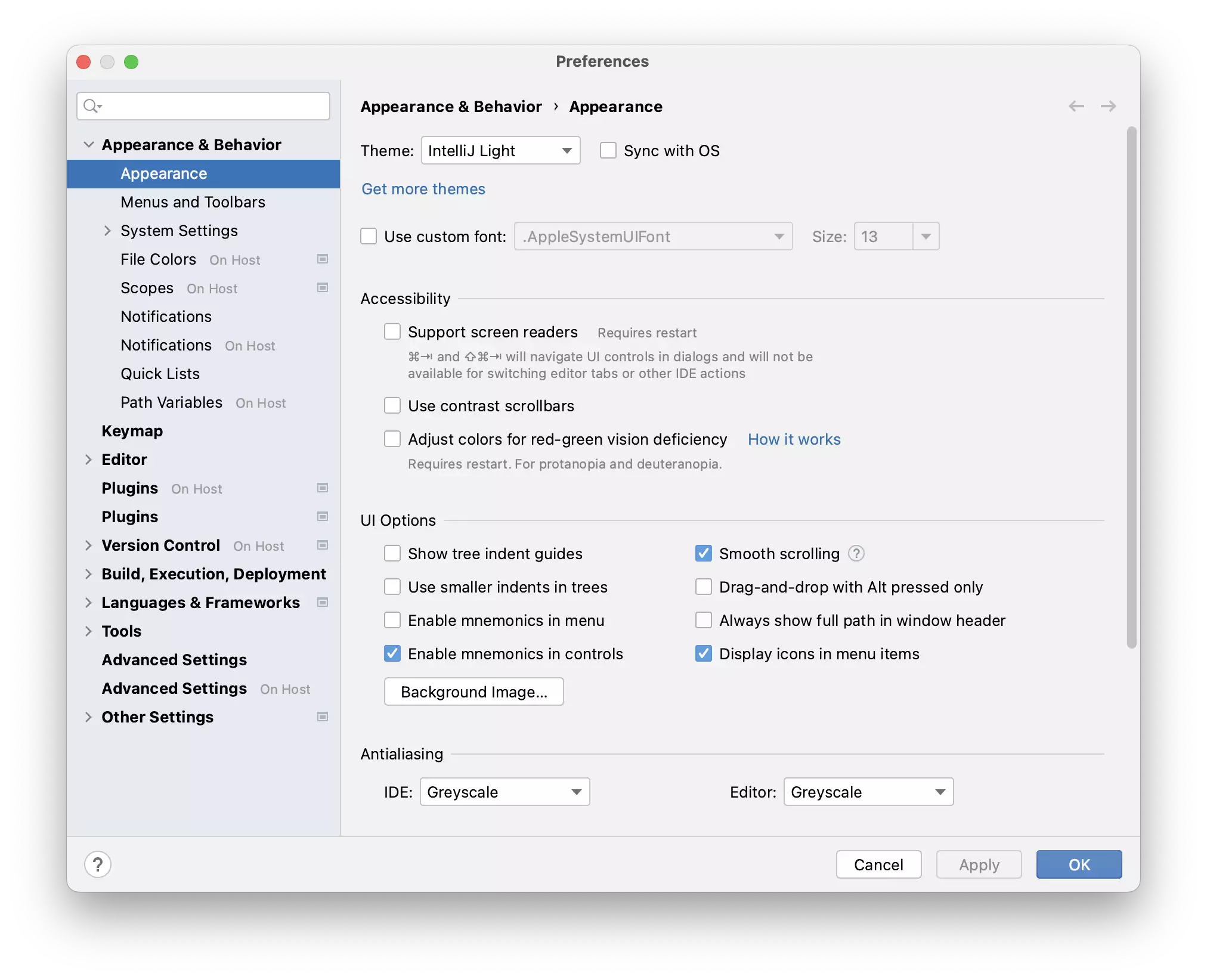
JetBrains client settings don't have <code>On Host</code> label.
On Rider backend
Settings configured on Rider backend are stored in a Gitpod workspace and haveOn Host label in the IDE settings.
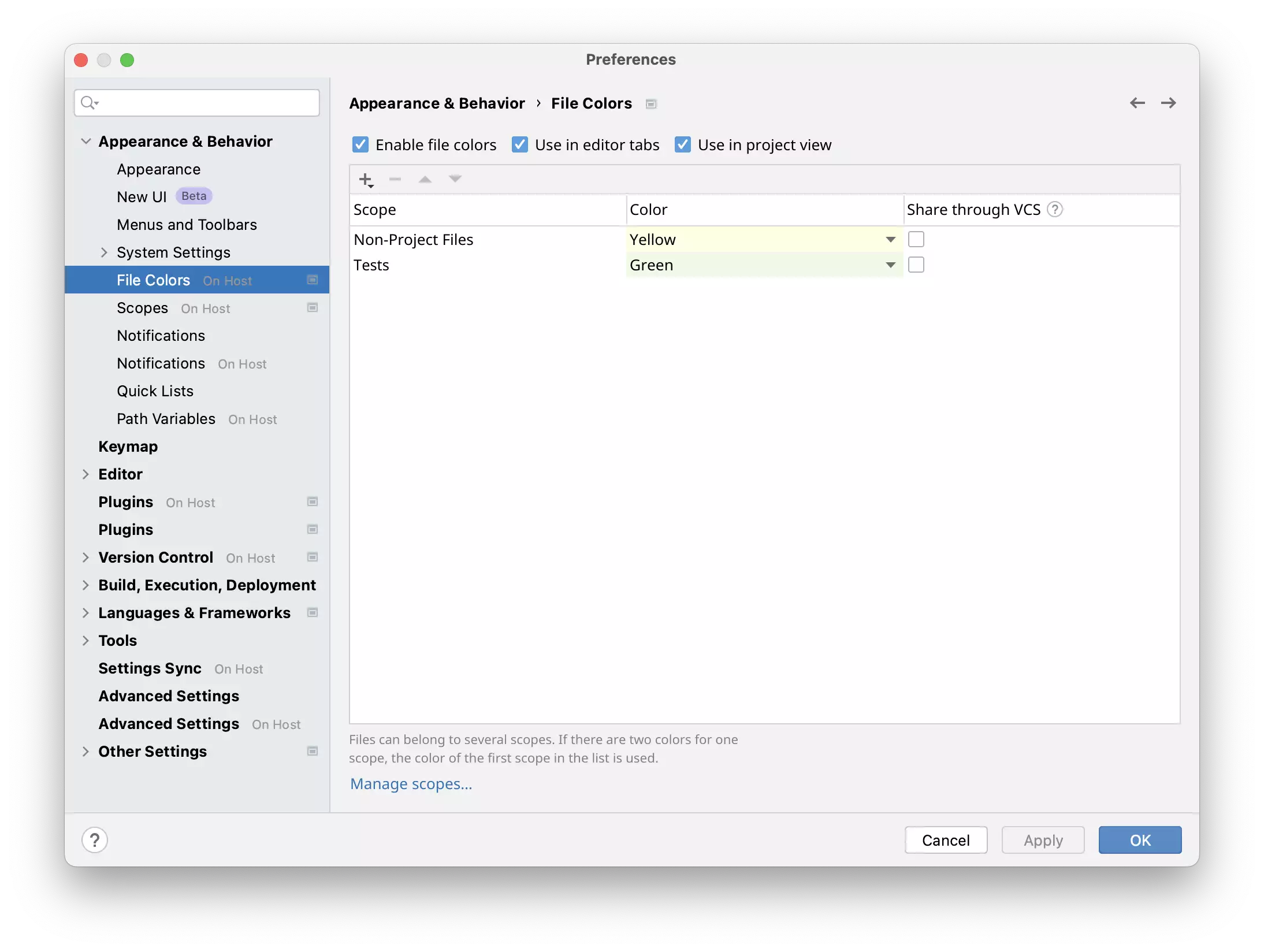
Rider backend settings have <code>On Host</code> label.
Configure IDE settings per project
Some IDE settings cannot be configured via environment variables or through setting vm options. These settings can only be set via the UI of JetBrains client, and must be manually copied to be synced between workspaces. The below steps detail how to configure your IDE settings for all the users of a given Gitpod project: Step 1: Manually use JetBrains UI to configure settings - Set your IDE settings as you normally would, using the JetBrains UI. Step 2: Find generated IDE settings - You will need to manually find any global settings generated by JetBrains backend within the following path:/workspace/.config/JetBrains<-latest>/RemoteDev-/<your-project-name>/options
Step 3: Move any relevant settings manually to a persistent location within your Gitpod project. Either via a Workspace Image, or persisted in the version control of your project, for example by committing settings data to GitHub.
Include relevant IDE settings in your Workspace Image
/home/gitpod/.gitpod/jetbrains/options- This location applies settings to all JetBrains products (IntelliJ IDEA, GoLang, etc)./home/gitpod/.gitpod/jetbrains/rider/options- This location will apply settings only to the given IDE, e.g. Rider.
/workspace/<your-project-name>/.gitpod/jetbrains/options- This location applies settings to all JetBrains products (IntelliJ IDEA, GoLang, etc)./workspace/<your-project-name>/.gitpod/jetbrains/rider/options- This location will apply settings only to the given IDE, e.g. Rider.
When locating and applying IDE settings, Gitpod will read the locations
specified above in priority order. The locations specified first are
overriden by the locations specified later.
Configure IDE settings per user
To configure IDE settings for your user only, and not all those using a project. Follow the instructions for configuring IDE settings per project, but instead use .dotfiles rather than a workspace image or source control to store your IDE settings.Indexing using Prebuilds
Currently, prebuilds for Rider are not supported. To leave feedback or check for updates, see gitpod/issues/6740.Workspace performance
When using a Gitpod workspace you might experience performance issues caused by:- An application using more resources than expected
- Resource consumption in adjacent containers running on the workspace node.
Workspace CPU and Workspace Memory.
The remaining metrics you can find in the Backend Control Center regarding the node that your workspace is running on, and not the workspace itself.
Performance information shown in the Backend Control Center is the same as
the information that is shown when running the command
gp top in your workspace, see the Command Line
Interface documentation for more.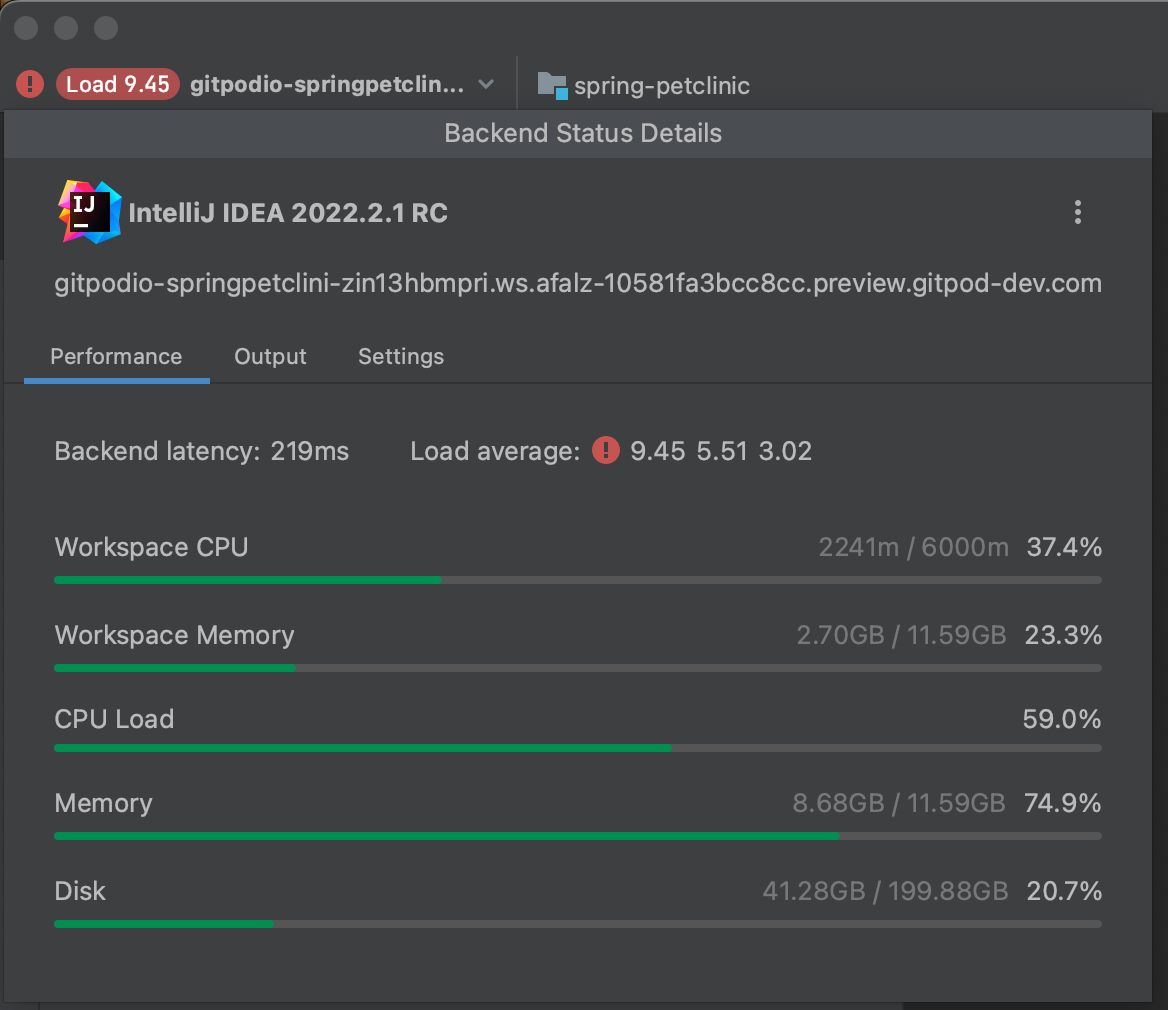
jetbrains performance
FAQs
- For the questions about supported IDEs and Editors in Gitpod, refer to FAQs.
- For the general questions about JetBrains Remote Development, refer to refer to the general IDE Rider FAQ.
Are there any JetBrains optimizations I can make if my workspace is slow?
Debugging performance can be challenging, as performance issues can depend on many factors such as how Gitpod is configured (if you’re operating Gitpod on Self-Hosted). However, there are some ways you can gather performance information and optimise your JetBrains IDE setup with Gitpod:- Firstly, to gather information on performance, you can view workspace performance metrics from within the IDE in the Backend Control Center, or by using
gp top. - You may also want to try adjusting the Max Heap Size allocated to the JetBrains Backend in the Settings tab of the Backend Control Center. If updating this setting helps your performance, you can set the
vmoptionsvalue for your JetBrains IDE in your.gitpod.yml.
If the performance metrics show that your workspace is hitting its resource
limits, and you are using Gitpod Self-Hosted, it might make sense to
consider changing the resource configuration for your workspaces. This can
be done via a config-patch. Configuring workspace resources is not yet
available on SaaS.

