AWS
Environment classes
Environment classes define the specifications of your cloud development environments run by AWS runners. They control computing resources like instance type and disk size to meet your development needs.
Default environment classes
Gitpod comes with several pre-configured environment classes for your AWS runners. These defaults offer a range of computing resources to support different development workloads. By default, Gitpod creates the following environment classes:| Class Name | Instance Type | Disk Size | Spot Instance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small | M6i Large (m6i.large) | 45 GB | No |
| Regular | M6i XLarge (m6i.xlarge) | 80 GB | No |
| Large | M6i 2XLarge (m6i.2xlarge) | 100 GB | No |
| Extra Large | M6i 8XLarge (m6i.8xlarge) | 200 GB | No |
| Extra Large Spot | M7i 8XLarge (m7i.8xlarge) | 200 GB | Yes |
| Data Science Large | G5 4XLarge (g5.4xlarge) | 300 GB | No |
| Data Science Large Spot | G5 4XLarge (g5.4xlarge) | 300 GB | Yes |
Creating custom environment classes
You can create custom environment classes tailored to your team’s specific requirements:- Navigate to your Gitpod organization settings
- Select Environment Classes under AWS runners
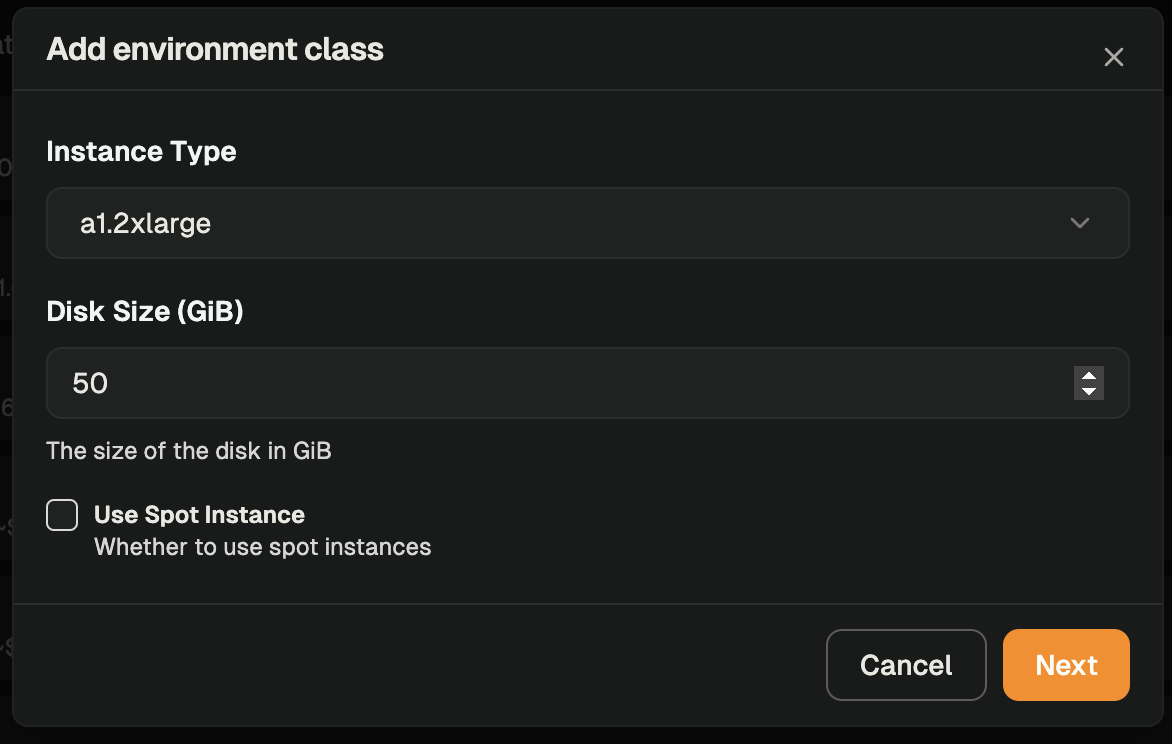
- Click Add Environment Class
- Configure the following:
- Name: A clear, descriptive identifier
- Description: Details about the purpose or resources
- Disk size: Storage capacity for the environment
- Instance type: AWS EC2 instance type determining CPU and memory
- Supports any x64 EBS-enabled instance type (e.g., t3.medium, m5.large, c5.xlarge)
Managing environment classes

Add a new environment class
Modifying environment classes
Once an environment class is created, only its name and description can be updated. To change configuration values like disk size or instance type, you must:- Create a new environment class with the desired specifications
- Optionally disable the previous class
Disabling environment classes
When you disable an environment class:- Existing environments using this class will continue to run
- Users cannot create new environments with this class
- Scheduled or automated processes cannot create new environments with this class
Using environment classes
Users can select environment classes when creating new development environments by:- Manually selecting the environment class during environment creation
- Using a project that’s configured to use a specific environment class
Supported instance types
AWS runners support any instance type that meets the following requirements:- Any EC2 instance with EBS volume support
- X64 architecture (Intel or AMD processors)
- General purpose:
t3.medium,t3.large,m5.large,m5.xlarge - Compute optimized:
c5.large,c5.xlarge - Memory optimized:
r5.large,r5.xlarge - Storage optimized:
i3.large,d2.xlarge
Considerations
- Regional availability: Not all instance types are available in every AWS region
- Quotas: Ensure your AWS account has sufficient quota for your chosen instance types
- Costs: Different instance families have varying pricing models
- Instance generations: Newer generations generally offer better price-performance ratio
- Storage: Use an instance type which has more storage than RAM.
Best practices
- Be prescriptive with your environment classes to standardize resources across your organization
- Limit the environment classes to what your teams actually need
- Create specialized classes for specific workloads (e.g., data processing, frontend development)
- Review usage patterns regularly and adjust available classes accordingly